Up to date 8 Jan 2023. I regularly replace this web page, so please seek advice from the present model. For mite therapy choices, search “Varroa Mite Administration”
Beekeeping in a Nutshell
I’ve tried to distill 50 yr’s of beekeeping expertise into a brief set of directions for beginning out with bees within the Sierra Foothills. This web page offers some fast step-by-step notes in your first yr of beekeeping, written particularly for these beginning with a nucleus hive or bundle bees bought from me, however is usually relevant.
Backside line: When you get a colony began, apart from including area, the 2 most vital issues to concentrate to are varroa administration and colony vitamin. Should you do that, most different issues go away.
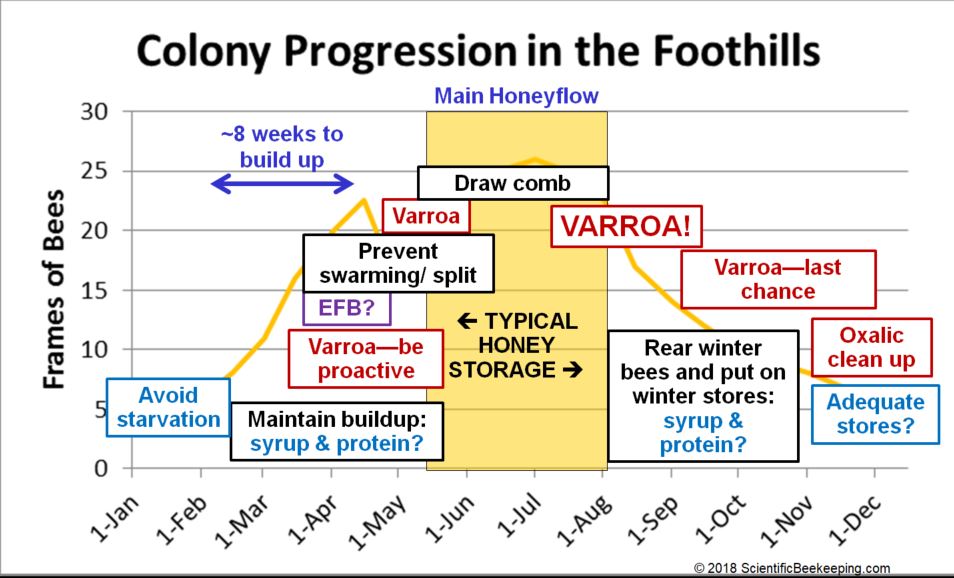
Beneath is a short visible of hive administration obligations within the Northern California Foothills. Should you stay someplace else, the timing of the honey circulation and size of winter might differ. I’ve written a step-by-step plan for colony administration additional down on this web page.
Beginning Out
First, educate your self! A honey bee colony is a residing animal that deserves to be cared for correctly. You might be starting beekeeping at a time during which honey bees are struggling to remain alive–beekeeping is harder than it was previous to the parasitic varroa mite (which invaded round 1990). Though honey bees are basically wild animals residing in a field offered by their “keeper,” bees are within the midst of an evolutionary battle because of the introduction of varroa (which utterly modified colony stress and virus dynamics). As well as, the bee inhabitants now faces the extra novel stressors of persistent European foulbrood, lack of forage in lots of areas, the results of local weather change (shorter winters), rising CO2 (which decreases the dietary worth of pollen), and maybe pesticide publicity (this concern is vastly exaggerated so far as most areas are involved, however might happen in areas with intensive industrial agriculture).
Aside from varroa, nevertheless, fundamental beekeeping practices have been properly found out way back, and I extremely suggest two traditional USDA publications for greatest administration practices. Bear in mind that each of those publications have been for the North, and would have to be adjusted significantly for the West and southerly areas, however the primary ideas nonetheless apply. Farrar’s Productive Administration of Honey Bee Colonies is a good learn for understanding the winter cluster and swarm prevention; Beekeeping in the USA covers all areas, and has an incredible part by Moeller entitled Managing Colonies for Excessive Honey Yields. I’ve linked these articles at Studying Supplies.
It’s harder to maintain wholesome bees than it’s to take care of commonest pets (for which you typically want solely to supply meals). The extra you perceive the biology of colony well being and dynamics, the extra profitable you will be at beekeeping. Bees see and reply to the world (environmental cues) very in a different way than do people. With the intention to be a greater beekeeper, I counsel that you just attempt to be taught to see the world by the eyes (and antennae) of the bee, and to “suppose” as does the honey bee superorganism.
What’s your motivation?
Please permit me to be frank. In case your motivation is to “save the bees,” please notice that the honey bee is in completely no hazard of extinction. Caring for a hive of bees requires a number of hours of husbandry a yr, involving opening and inspecting the frames inside, and getting stung. Retaining your bees alive and wholesome nowadays requires administration for the varroa mite–most novices fail at this, and their colonies die an unsightly loss of life.
The primary suggestions that I get from first-year beekeepers is that they didn’t notice how vital it was to observe and management varroa of their hive — most novices lose their first hive to the mite.
So in case your motivation is to assist the bees, until you’re prepared to supply a hive with good husbandry, you’d do extra service to bees, different pollinators, and the surroundings by planting flowers and flowering shrubs and bushes, supporting small farmers, shopping for native produce, minimizing your carbon footprint, and telling your representatives to assist the EPA.
However, the maintaining of honey bees provides one a “tangible connection to the wild.” Should you’re prepared to take the time, the honey bee may also help to attach you to Nature, and to the enjoyment of experiencing how this fascinating social insect manages to eke out a residing.
“Remedy-Free” beekeeping
I stored bees “treatment-free” for 20 years previous to the arrival of varroa, and my aim is to have the ability to achieve this once more in my lifetime. In the direction of that finish, I’m an enormous proponent for breeding bees for the traits concerned in pure resistance to varroa, and am critically concerned in my very own breeding program. That mentioned, most traces of honey bees as we speak will succumb to the varroa/virus advanced inside a yr or two of beginning the hive, until real looking measures are taken by the beekeeper to cut back the mite inhabitants. Please learn my article “The Varroa Drawback Half 6b–Small-Scale Breeding,” during which I talk about a number of the misconceptions usually advocated by well-intentioned (however biologically misinformed) “treatment-free” promoters.
If in case you have an remoted apiary, or are lucky sufficient to get a queen with the precise genetics, your colony might survive with out therapy. Sadly, this typically doesn’t occur, and most starting beekeepers lose their colonies to varroa. That is utterly avoidable, and will be prevented by common monitoring of your hive for its diploma of varroa infestation with alcohol washes (my most well-liked methodology) or a well-done sugar shake. If thus indictated, there are a selection of protected and efficient (and organically-approved) merchandise that can be utilized to cut back the mite inhabitants (detailed additional down).
We love our bees, and hate to ship our lovely nucs off to sure loss of life as a consequence of beekeeper negligence. Please, monitor your colonies for his or her varroa degree from late June on, and assist them to outlive! Please be a accountable beekeeper–colonies which can be allowed to die from varroa damage the encircling beekeeping neighborhood.
Books
There are a number of good novices books.
First Classes in Beekeeping, Dadant. Commonplace newbie reference.
The Beekeeper’s Handbook by Diana Sammataro & Alfonse Avitabile. Many suggest this one.
Storey’s Information to Beekeeping. Straightforward studying model, simple info.
Beekeeping for Dummies. I haven’t but learn, however a number of novices have beneficial.
Honey Bee Hobbyist by Norm Gary—good general understanding, fairly than how-to.
Homegrown Honey Bees by Alethea Morrison. A enjoyable journal of the experiences of a first-year beekeeper. The writer ran it by me for accuracy previous to publication, so good data.
A E book of Bees, Sue Hubble–lovely prose about being a beekeeper
And naturally, ScientificBeekeeping.com. Though I’ve but to summarize my many articles right into a guide, I counsel that you become familiar with bees, beginning with how the colony manages its labor pool, feeds itself, varroa administration, The Guidelines of Beekeeping, and for a deeper understanding of the biology of the hive over the course of the yr, my Colony Buildup and Decline sequence.
Discover a Mentor
Beekeeping is tough to be taught from a guide, and the right dealing with of bees to keep away from extra stinging much more tough. The perfect factor to do is to recover from the innate human concern of bees and of being stung. Bees sting. You wish to hold bees. You’re gonna get stung, so get used to it! Skilled beekeepers typically really feel {that a} common dose of bee venom improves their well being and properly being.
HIVE INSPECTION
I strongly counsel that you just discover a mentor who can display dealing with approach. Discover a mentor who doesn’t usually put on gloves or a lot protecting gear. You wish to be taught to method your bees in a cooperative mindset, fairly than an adversarial method. Should you be taught whereas absolutely protected with gloves, you’re going to get unhealthy habits, because it prevents the bees from supplying you with “reminders” that your approach is sloppy or disrespectful to the hive.
Hive inspection on sunny days ought to contain minimal stingings, however I’d shoot for a number of dozen stings a season with a purpose to keep away from sensitizing your self to bee venom (beekeepers who obtain only some stings a season set themselves up for true bee sting allergy late on). Study to make use of smoke gently however appropriately. Transfer as if you might be working towards Tai Chi–no sudden actions. The purpose is to keep away from going previous the bees’ menace response threshold. At that time they may begin supplying you with “warning bumps” or stings. Study to acknowledge these warnings.
Tools
You’ll want a veil — defensive bees intention for the highest of the intruder. Essentially the most painful locations to be stung are all above your shoulders. Study to work bees barehanded, however put on a veil till you now not react to bee stings.
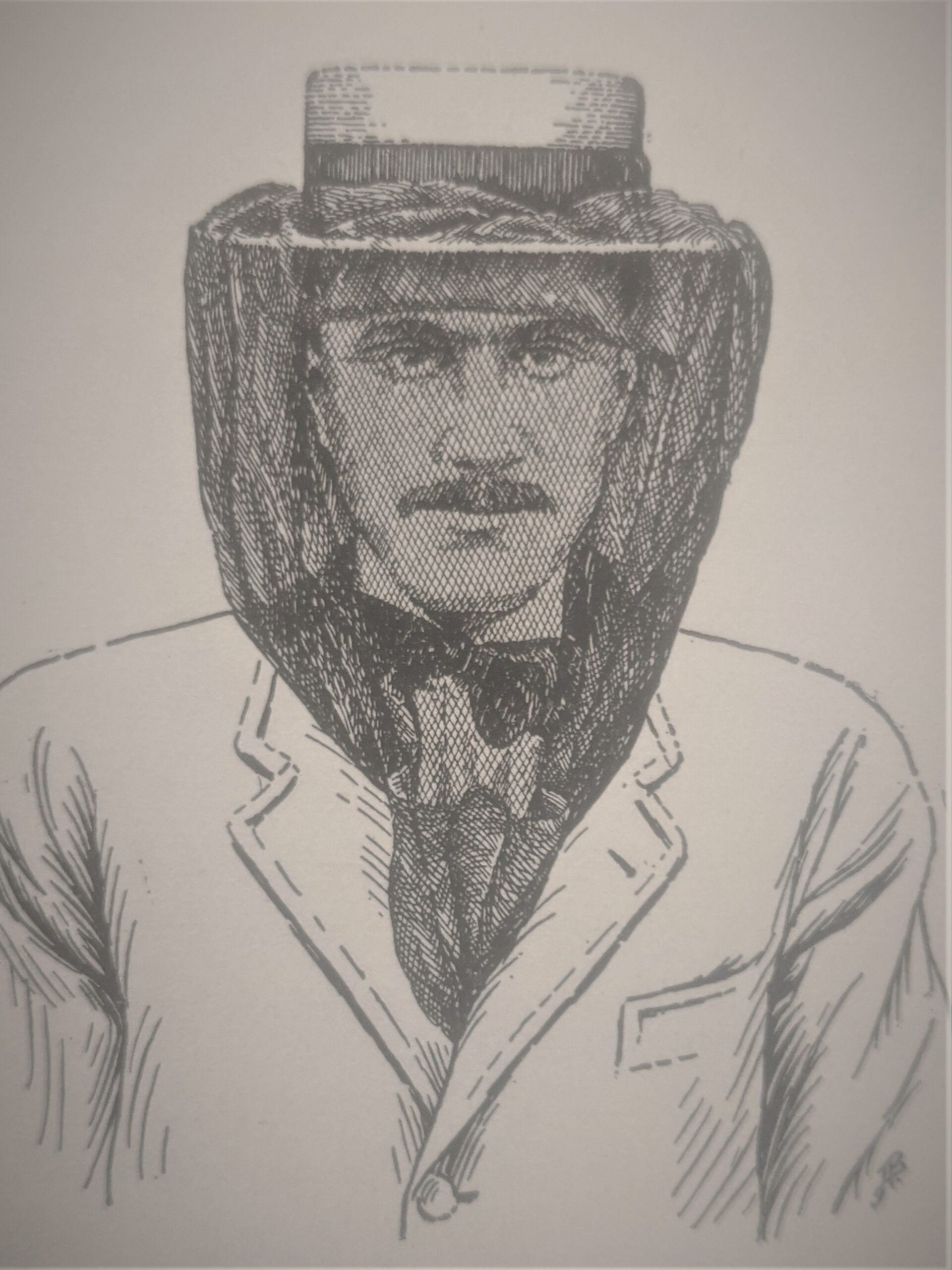
Picture is vital — the well-attired beekeeper seems to be sharp! Bow tie is non-obligatory.
Drawing from the guide Beekeeping, by E.F. Phillips 1921.
I counsel a light-weight hooded jacket (we haven’t examined all of them, however just like the (widely-available) Eco-keeper hooded bee jacket (proven beneath). FWIW, I’ve no excited by selling any merchandise, however am blissful to inform you which merchandise we use in our personal beekeeping enterprise of 2000 hives.

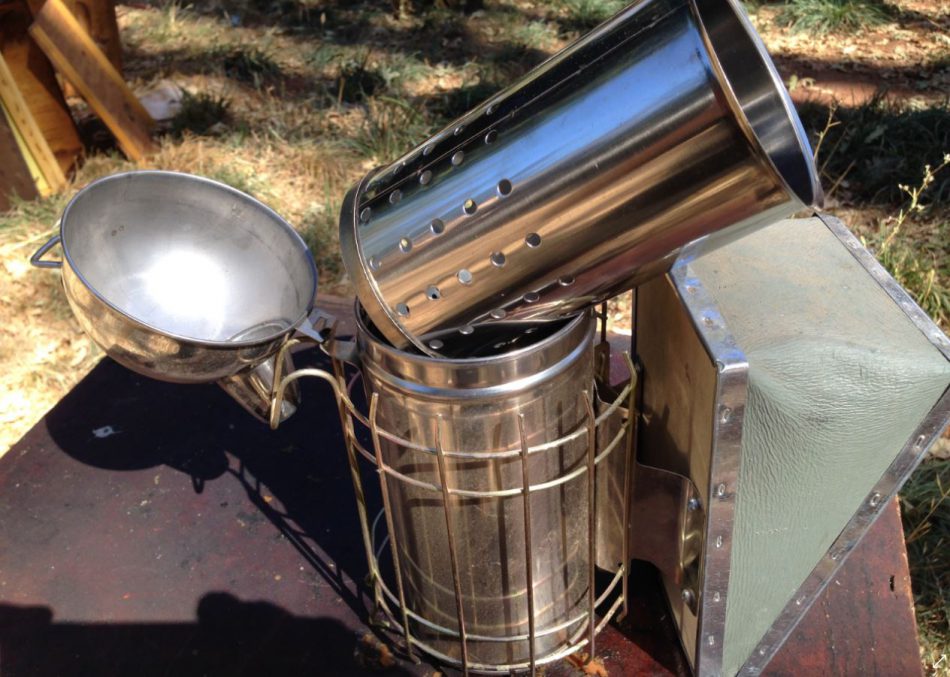
A smoker — So far as people who smoke, I personally choose dome-top fairly than cone-top (funnel-shaped) people who smoke, within the 4″ x 7″ measurement (4 x 10 is simply too massive and awkward). Dome prime people who smoke higher direct the smoke and don’t burn by the gas as quickly as do cone prime). I like a stainless-steel smoker, with a protecting basket round it, with a sq. non-plastic bellows that’s roughly degree with the underside of the smoker, in order that it doesn’t are inclined to tip over (much like that proven beneath).

Word: I do not suggest the stainless people who smoke with full inside insert, similar to proven beneath–they don’t work properly! You need one with the perforated backside plate with three legs. Examine for what variety of insert is inside earlier than ordering!
The hive software — the smoker and hive software are the one instruments that I typically carry (plus a cigarette lighter to gentle the smoker). I choose the curved-end hive instruments as proven (fairly than flat hook-end instruments)–you are able to do every part with them.
 I vastly choose instruments with a 1/2″ offset fairly than the extra frequent 3/4″ curve, and I hold that edge sharp for scraping off propolis. I maintain my hive software to make use of the curved finish for prying aside frames, because it offers you extra leverage and management. I particularly just like the Jero model 7-1/2″ hive software for summer season work whenever you don’t want a whole lot of leverage to interrupt the propolis; I exploit a ten″ software when it’s cooler. Warning–Jero’s come actually sharp, so first rub the flat finish in opposition to a rock; go away the curved finish sharp.
I vastly choose instruments with a 1/2″ offset fairly than the extra frequent 3/4″ curve, and I hold that edge sharp for scraping off propolis. I maintain my hive software to make use of the curved finish for prying aside frames, because it offers you extra leverage and management. I particularly just like the Jero model 7-1/2″ hive software for summer season work whenever you don’t want a whole lot of leverage to interrupt the propolis; I exploit a ten″ software when it’s cooler. Warning–Jero’s come actually sharp, so first rub the flat finish in opposition to a rock; go away the curved finish sharp.
Gloves — greatest to be taught with out them, however I like to recommend vinyl (particulars beneath) or goatskin. Use Vaseline to maintain leather-based gloves versatile–it’s higher than any fancy therapy available on the market, and doesn’t add odor.
You may be a much better beekeeper as quickly as you be taught to work with out gloves, however I counsel that you just be taught to take action by working small colonies beneath excellent situations. Underneath different circumstances strive utilizing 5 mil white nitrile, long-cuff gloves.
I’ve been proud of the 2 manufacturers above. Every feels a bit totally different, however I can’t say that I choose one over the opposite. These gloves forestall most stings, are lengthy sufficient to tuck beneath the cuff of your jacket (I like to recommend a hooded jacket), and are remarkably sturdy (I’ve gotten 4 full days of laborious work out of some pairs).
We actually like these gloves after we are working bees in chilly or wet climate (we hardly ever put on gloves throughout heat climate). I placed on a glove throughout heat climate for the photograph above–sure, they get a bit sweaty, however your dexterity is so a lot better than with leather-based gloves. Should you want to put on leather-based gloves, get snug-fitting goatskin gloves.
You don’t want to keep away from stings–that can solely predispose you to eventual bee sting allergy. Working with gloves means that you can get into unhealthy habits–when gloveless, the bees will patiently remind you every time you make a mistake. Should you’re getting stung, you’re doing one thing mistaken (this doesn’t apply a lot with Africanized bees). It might be laborious for novices to imagine, however as soon as your immune system will get used to common stinging, your physique misses it when it doesn’t get its common doses of bee venom.
Dealing with Ideas:
Smoking the Hive
Neglect about going “smoke free”–correct, gentle use of smoke is the beekeeper’s greatest software. You solely want to make use of slightly, however apply that little bit instantly upon opening any a part of the hive–timing is every part!
You solely must smoke the guard bees–bees in the midst of the cluster hardly ever sting–apply light smoke to these on the periphery. Take a look at their “faces”–if they’re taking a look at you, then they’re conscious of you! Slightly little bit of smoke goes a great distance — don’t over smoke your colony — use solely sufficient smoke to get the bees off the highest bars, and in order that none are taking a look at you.
By no means attain for a body if there are bees taking a look at you. Discover the bees within the photograph above which can be taking a look at you. They’re guard bees, and since they’re taking a look at you, they’re conscious of you. Give them a mild puff of smoke to show them away from you. Solely whenever you don’t see any faces taking a look at it is best to you attain in direction of a body. Keep watch over the bees, and after they begin to have a look at you once more, give one other light puff of smoke.
Guarantee that your smoke comes out cool, WHITE, and DENSE. Bees don’t reply to weak or gray smoke like they do to dense white smoke. Many beekeepers use burlap, however I dislike the odor. Many pure supplies work properly–ask an area beekeeper. My favorites are pine needles fluffed by automotive tires on an asphalt highway after the primary autumn rainstorm, punky oak wooden, eucalyptus bark, oak leaves, or wooden pellets (tougher to gentle, however burn for a very long time).
Working the hive
Freshmen ought to all the time put on a veil! (Because of beekeeper Trish Harness for this suggestion). Essentially the most painful locations to be stung are all in your head, and that’s precisely the place defending bees intention! Till you’ve construct up “immunity” to stings, all the time put on a veil.
Method bees with respect, however recover from your concern of them as rapidly as potential. Stings are the bees’ manner of telling you that you’ve made them suppose that they should defend their colony–when you be taught to not give them purpose, you may make it seem like magic.
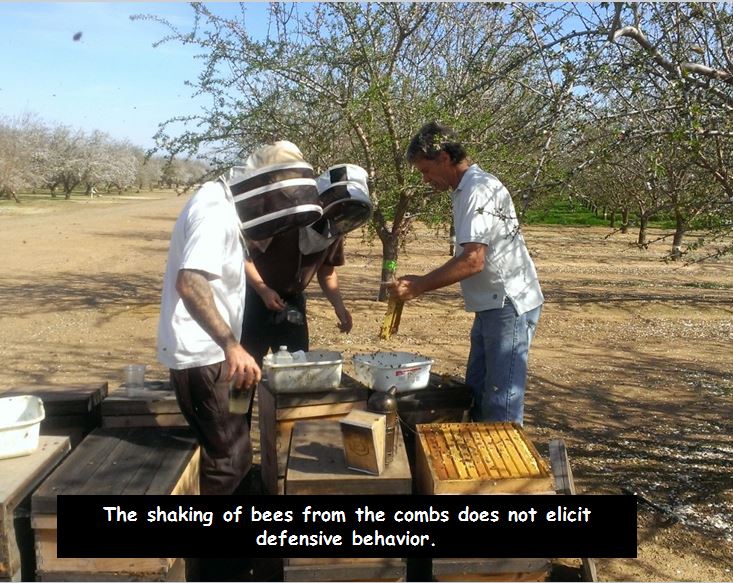
In my novices demonstrations, I get individuals over their preliminary concern by my instance of sporting solely shorts and a tee shirt, opening a hive,, after which shaking a bathtub stuffed with bees from the comb, then ladling scoops of bees with my naked hand into their naked arms–nobody ever will get stung. After this demonstration, everybody is much extra relaxed across the bees. However I do know precisely what I’m doing.
And I’ve been stung so many occasions that I now not swell up or itch after a sting (OK, slight momentary swelling when stung on the lip or eyelid). One will get used to stings to the arms and elsewhere, however the ones to the face nonetheless damage like hell for a couple of minutes. So though you will note many skilled beekeepers working with out veils (as a result of it’s a lot simpler to see the queen, eggs, and so on.), I strongly counsel that novices all the time put on a veil till they now not swell in response to stings. And make it possible for any guests put on a veil. Sensible tip: put in your veil earlier than you enter the apiary, and don’t take away it till you might be out of sight of the hives (that is when many get stung to the face). We actually just like the hooded jackets that unzip from the entrance and permit us to flip the hood ahead or backward.
Typical bee working for my sons and I (we’re in an almond orchard, performing alcohol washes for varroa). Word that when it’s heat, my sons sometimes throw a hooded veil over their heads, unzipped from the jacket.
Transfer easily–such as you’re doing Tai Chi. Bees solely sting after they really feel that you’re threatening their hive. So don’t do something threatening! Quick or jerky actions seem threatening. All the time use smoke, however use it sparingly. The one bees that can typically sting are the guard bees on the periphery of the cluster–particularly on the entrance and on the prime bars. Bees that aren’t taking a look at you aren’t excited by you. Should you see bees taking a look at you, give them slightly puff of smoke and wait till they flip away from you. It is just protected to choose up a body if there aren’t any bees taking a look at you.
Bees will usually fly at your arms or face and provides “warning bumps” previous to precise stinging. Take note of what they’re telling you–BACK OFF! They both don’t wish to be disturbed at that second, or you haven’t used sufficient smoke, otherwise you’ve been too tough.
If there are bees taking a look at you, warning bumps, stinging, or the odor of alarm pheromone, STOP WHAT YOU ARE DOING! Don’t hold going, or issues will rapidly worsen–you don’t wish to go there! Give the bees an opportunity to relax, and for alarm pheromone to dissipate. Give the highest bars a light-weight puff or two of smoke till there aren’t any bees going through you. Should you can’t get them to relax, then simply shut the hive up for the day.
One of the best ways to learn to work gently with bees is to fastidiously watch an skilled beekeeper who doesn’t often put on gloves (or veil). Such a beekeeper has discovered the best way to work bees with care and respect. Those that all the time put on gloves and full gear usually have very unhealthy habits. I strongly counsel that you just be taught to work bees barehanded in good climate–skinny latex or nitrile gloves are a great way to eradicate most stings, however nonetheless get a “really feel” for the bees.
The Guidelines
Q: What “ought to I do?”
A: There aren’t any “shoulds” in beekeeping apart from working towards good animal husbandry. Bees want solely a dry cavity, meals (nectar, pollen, or syrup and pollen complement if missing from pure sources), and parasite administration. My fundamental rule is to not do something until you utterly perceive the rationale that you’re doing it!
One can find on the web a plethora of opinions (usually strongly expressed) on the “proper manner” to maintain bees. On the whole, the extra emphatic the writer, the much less I’d belief the data. For a overview of the principles in line with the bees, see The Guidelines and The Guidelines Redux.
My recommendation–focus on (1) varroa administration and (2) vitamin (particularly within the late summer season), and achieve this proactively–earlier than mites or poor vitamin have critically careworn the colony.
Getting Began
I strongly counsel that you just begin with two deep Langstroth brood chambers (to determine the brood chamber), and later “medium” honey supers over a queen excluder (a number of causes). Such tools has actually stood the take a look at of time (for the reason that mid 1800’s) and is by far the best option to be taught to maintain bees. You possibly can strive different programs (prime bar, Warre, and so on.) later, after you’ve skilled success with “customary” tools. If weight (of the containers) is a matter for you, I counsel utilizing 8-frame Langstroth tools (similar as above, however a narrower, lighter field), fairly than utilizing medium supers for the brood chamber.
Location
Place your hives in a sunny location with morning solar, in order that they’ll get an early begin at foraging within the morning. Should you stay in an particularly scorching space, they may profit from afternoon shade. Hives will do OK within the shade, however are rather more “pissy” to work. Place the hives in a dry space with good air drainage. The perfect hive stands are two 8″x8″x16″ cinder blocks, positioned flat sides down, with the hive tipped barely ahead for drainage. Don’t place a couple of hive on a stand, as vibrations from working will transmit by way of the stand to the opposite hives. If in case you have neighbors, place a fish pond with aquatic crops and floating wooden as a water supply in your bees (in order that the bees gained’t trigger issues together with your neighbors).
Should you stay in an space with bears, you MUST shield the hive. Plans for a cheap bear fence are right here.
The Plan — Step-by-step
A nuc or bundle comes with a vigorous younger queen and a cluster of bees. A nuc, as a consequence of already having brood, will develop rather more rapidly. In case you are a first-time beekeeper, I counsel that you just request a weak nuc, so that you’ve extra time to be taught earlier than it grows into a big and extra defensive colony.
Beneath is an overview of your administration plan. Additional down are extra particulars.
First-year steps:
Institution
- Set up the nuc/bundle right into a brood chamber. Add drawn comb when you’ve got it, in any other case frames of basis (wax-coated plastic basis is by far the best to make use of). Basis is just not essential, nevertheless it makes beekeeping MUCH simpler. Place 10 frames whole within the hive physique, all all the time squeezed tightly collectively.
- Except there’s a robust nectar circulation on, feed the colony as a lot 1:1 sugar syrup as they may take (at the very least a half gallon a day if on basis). This may permit the colony to supply the beeswax essential to attract comb. A powerful nuc missing honey shops can starve in a day — make it possible for they’ve a comb of honey when put in, or feed at the very least a gallon of sugar syrup instantly.
- Proceed feeding till all 10 combs are drawn, and the outer two combs are crammed with “honey.” Solely then will you add the second brood chamber (by this time all 10 frames will sometimes even be coated with bees).
Charge of colony development: A robust nuc stuffed with sealed brood can develop explosively! It will probably fill 1o frames in lower than per week. That’s why I counsel that first-timers ask for a weak nuc — in order that they’ll take pleasure in opening it up just a few occasions per week and watching it develop.
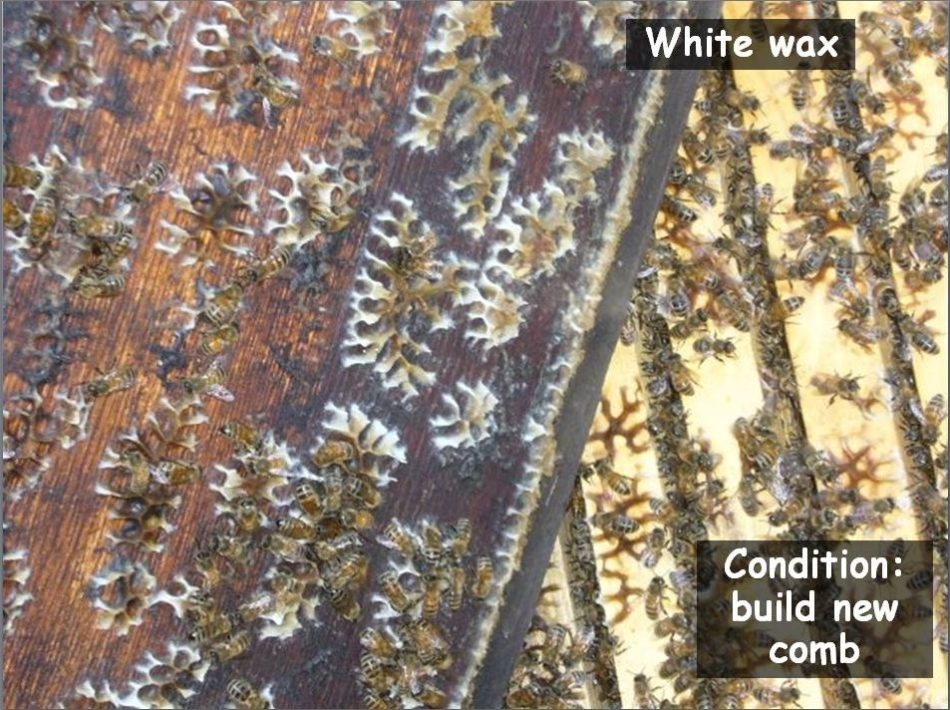
One drawback for novices is {that a} new hive is way simpler to handle on already “drawn” comb than in case you are beginning with basis. A powerful nuc, if not fed sufficient syrup to attract comb, might really feel “crowded” and swarm! Feed the colony sufficient in order that they’re producing “white wax” and drawing comb repeatedly.
Word: it’s typically not essential to feed colonies sugar syrup. However, bees LOVE sugar syrup, and it’s considered one of our greatest administration instruments. If there is no such thing as a pure nectar circulation occurring, the feeding of syrup will permit a colony to proceed rising and drawing basis, or to placed on winter shops. The extra hives within the neighborhood, the extra seemingly that there will probably be nectar dearths, since small rising colonies can not compete in opposition to massive established colonies.
Including the second brood chamber
- Add the second brood chamber — with 10 frames of basis or drawn comb, all squeezed collectively. On the whole, you’re going to get straighter combs for those who don’t combine frames of basis with frames of drawn comb.
- At this level you’ll be able to resolve whether or not to proceed feeding syrup, or if the honey circulation has begun, to permit the bees to retailer pure honey. Should you select the latter, you’ll be able to later extract a number of the honey, after which feed syrup to exchange it for winter shops.
Supering for honey
- On the whole within the West, a nuc or bundle gained’t develop bigger than two deeps excessive within the first yr. But when it does, you’ll be able to place a queen excluder over it (I like queen excluders), after which place a medium tremendous on prime for honey assortment. Tip: bees are detest to attract basis above a queen excluder if there’s a band of honey within the combs instantly beneath the excluder. If so, rotate some brood combs from the decrease brood chamber into the center of the higher brood chamber, in order that brood is correct up in opposition to the excluder. This may encourage the bees to cross by the excluder and draw comb. Vital be aware: bees is not going to draw basis till each drawn cell within the containers beneath is crammed with nectar! There aren’t any methods to induce them to attract basis in any other case.
June/July administration
- Beginning in June, carry out alcohol wash or sugar roll to observe the mite degree. Deal with if greater than 6 mites per half cup of bees.
- Your first-year aim is to construct the colony to a double-deep brood chamber, with the higher field principally crammed with honey to supply winter shops.
August administration
- Management varroa! The honey circulation is often over, until you might be surrounded by star thistle, or incense cedar.
September/October administration
- Whereas the climate remains to be heat, be sure the colony has sufficient honey shops for winter. The higher brood chamber must be largely stuffed with honey, with the broodnest all within the decrease brood chamber. If not, begin feeding heavy syrup. Except there’s loads of pollen coming in, we additionally will feed high-quality pollen sub (2.5 kilos each 10 days) to permit the bees to brood up closely. It’s the bees that emerge from brood reared in October that can type the winter cluster.
Word: for those who stay within the Bay Space, chances are you’ll get a big eucalypt honey circulation in November. Discuss to native beekeepers for recommendation.
December administration:
- Varroa: as soon as a lot of the brood has emerged, apply an oxalic acid dribble or vaporization in order that the colony goes into winter with a minimal mite load.
Extra detailed administration suggestions
Putting in the bees
Congratulations, you’ve simply bought both a high quality nucleus colony (“nuc”) or a shook swarm (“bundle bees”) with a newly-mated queen from chosen inventory!
Warning: A powerful nuc is filled with brood and able to develop explosively! You might must switch your nuc into a bigger hive inside a day or so, or they might swarm. And until they’ve at the very least half a body of honey saved, they might starve if not given some sugar syrup.
Some nucs (and all packages) have the queen caged. In that case, take away the sweet cap whenever you get house to permit the bees to chew by the sweet and launch the queen. However do NOT take away the sweet cap if the bees are tightly balled over the cage, indicating that they haven’t but accepted the queen–wait one other day till they’re strolling evenly over the cage.
Set up the nuc within the middle of a brood field with extra frames to fill the field. Maintain the frames of the nuc of their unique order. Be very cautious to not crush the queen–a considerable share of queens are by accident killed by new beekeepers in the course of the preliminary switch course of.
For a bundle, there are a zillion suggestions for specifics as to the best way to set up the bees. It makes little distinction in case you are putting in solely a single bundle if there aren’t any different hives instantly close by (if there are, set up late close to nightfall to keep away from drift of bees to the established hive). On the whole, elevate out the feeder can to take away the queen cage, and grasp the cage (use a grocery retailer twist tie or toothpick) from the highest of a middle body. Then shake the bees out of the cage into the hive (you’ll be able to briefly take away frames). Use no smoke in the course of the set up. Then substitute the hive cowl (you’ll be able to place the bundle with the opening subsequent to the doorway to permit the remainder of the bees to seek out their manner into the hive.
Feeding your bees
Your nuc might arrive hungry–test to make it possible for at the very least one of many outer combs accommodates saved honey. If there’s a good nectar circulation on when your nuc is put in, there is no such thing as a must feed, however the feeding of sugar syrup to the small colony frees the bees from the necessity to forage for nectar, they usually can use their efforts as a substitute to gather pollen, rear brood, produce beeswax, and draw out comb. The manufacturing of beeswax with a purpose to “draw out” the frames of basis into “drawn combs” requires an excessive amount of sugar (whether or not from nectar or syrup). Due to this fact, it’s typically a good suggestion to persistently feed sugar syrup to the brand new colony till all of the frames within the decrease field are absolutely drawn.
A rising colony needing to attract basis can make the most of extra sugar syrup than you’ll be able to think about (gallons)–feed it as a lot as it would eat till all 10 frames within the decrease brood chamber are drawn out.
Right here’s the artwork: the bees can solely construct comb on warmed frames, so until the climate is sort of heat, they gained’t have the ability to draw comb outdoors of the cluster. Should you overfeed, the bees will fill the broodnest stuffed with nectar, thus stopping the queen from laying extra eggs. So what you wish to do is to observe the broodnest, and feed sufficient syrup for the bees to be creating “white wax” on the edges of the cluster (that means that the quantity of incoming nectar and syrup, relative to the quantity of free open cells, is stimulating them to activate their wax glands). As soon as the sealed brood of the nuc begins rising, the colony (cluster measurement) will begin increasing quickly, and you’ll then feed closely to permit them to attract comb.
So at first, the colony might have maybe a cup of syrup per day. Afterward, it could take a gallon a day. As soon as all of the frames within the first brood chamber are drawn, then it’s as much as you whether or not you want to proceed to feed. Sometimes, within the Sierra, the primary honey circulation could also be on by that point, and chances are you’ll want to accumulate some honey. You possibly can all the time return to feeding later within the season (July), if essential, to assist them to attract out all of the combs within the higher brood chamber, and to placed on honey shops (in Sept and Oct) for winter.
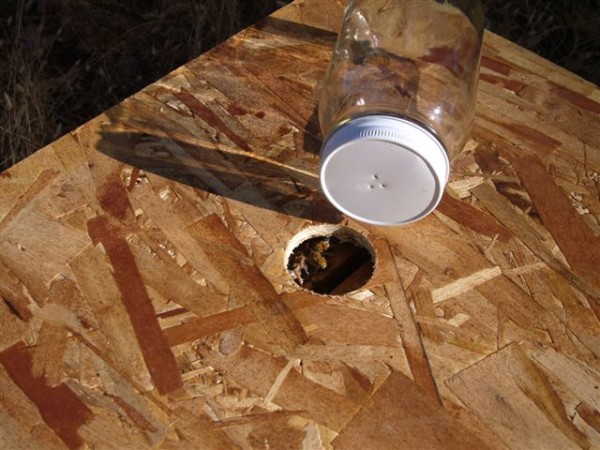
I suggest making a devoted feeder lid—make it from a 16¼” x 20” piece of plywood, with an approx. 1½” gap within the middle. Use this lid briefly rather than your common lid(s). Make a feeder bottle from any wide-mouthed quart jar, with about three small holes punched intently collectively within the middle of the lid. To make use of the feeder, fill the jar 2/3rds stuffed with white granulated sugar (feed no different sugars*), then add scorching faucet water till practically full. Place your finger over the holes, and shake ‘til the sugar’s dissolved. Invert the jar, centered over the opening within the feeder lid. Usually, feed as a lot syrup because the bees will take (at the very least a quart per day, usually extra).
*Nectar accommodates sucrose, fructose, and glucose–all of which bees can simply digest and make the most of. Bees can not digest a number of the advanced sugars or minerals in uncooked or brown sugar, some fruit sugars, and meals waste sugars–feeding any of those might trigger yeast infections within the bee hindgut and dysentery–additional information right here. Outdated honey might include poisonous HMF or AFB spores, so is just not beneficial. Every sort of sugar syrup has benefits and downsides so far as granulation points, and so on. It’s typically best for the hobbyist to feed sucrose syrup, utilizing plain previous “white” granulated cane or beet sugar (ignore the web chatter about purported GMO points).
Use “gentle” syrup for stimulation, “heavy” syrup for winter shops. Gentle syrup is 1 half sugar: 1 half water (by both weight or quantity)–that is much like essentially the most sugar-rich pure nectars; heavy syrup is 2 elements sugar:1 half extremely popular water, and is rapidly transformed by the bees to “honey” for winter consumption. Bees additionally do very properly on a industrial sucrose:HFCS combine, similar to Mann Lake’s Prosweet, generally utilized by skilled beekeepers (different producers carry totally different sugar merchandise at totally different branches, so I can’t make blanket suggestions).
C&H Baker’s Drivert (a dry flaky product from bakeries) makes for an incredible dry feed for stimulation–helpful in nucs. Baker’s fondant, laborious “sweet boards,” and even granulated sugar over newspaper can be utilized for winter feed (though merely leaving the bees sufficient pure honey is often greatest, until they’ve saved honeydew, which may trigger dysentery).
I’ve seen no proof of profit from including acid, important oils, or purported stimulants or well being dietary supplements to the syrup. I do add a half tsp of unscented family bleach per gallon to gentle syrup fed throughout scorching climate, with a purpose to forestall dangerous microbial development within the feeders. The bees seem to like chlorine!
It might by no means be essential to feed sugar to your colonies–I stored bees for 25 years with out ever feeding syrup. However then I discovered that syrup will be of nice assist to the bees when there is no such thing as a nectar circulation, and may vastly help colonies in “getting going” and drawing comb.
It doesn’t matter what you feed, be sure you hold your honey pure by by no means feeding syrup in any manner that it might presumably get into honey to be extracted!
An instance of a easy feeder jar and momentary hive cowl for feeding. By making the opening smaller than the dimensions of the lid, loads of beespace is left above the highest bars. Use a wide-mouth jar for stability.
Administration abstract for the foothills
Hive Inspection
For greatest queen survival, you shouldn’t disturb the brand new colony for just a few days (apart from feeding). Examine the colony after per week. Use little smoke and minimal disturbance. If all’s properly, the bees ought to have began drawing out recent comb, there must be brood of all ages, together with white larvae and eggs. Word that eggs are very tough for the newbie to see, particularly in opposition to new comb. The presence of any eggs, or younger larvae in royal jelly, means that you’ve a queen, and all’s properly—you needn’t really see the queen!
Q: How usually “ought to” I examine my colony?
A: There aren’t any “shoulds” in beekeeping. You might be studying about beekeeping. You possibly can be taught some issues from books, however there’s nothing just like the hands-on expertise that you just get from intently observing what’s going on contained in the field. So open your hive as usually as you’ll be able to (each different day is OK) as long as you employ solely sufficient smoke to maintain the bees from taking a look at you, and deal with the frames fastidiously and gently. Positive, such frequent opening is disruptive to the bees and will lead to some extent of queen losses, however it’s the solely manner you’ll ever develop into a superb beekeeper. It’s far simpler to watch the expansion of a small nucleus colony than it’s to tear right into a hive when it’s big. So get in there and watch your colony develop! Study to acknowledge the ages of the brood, recent eggs, the enlargement of the broodnest, pollen shops, comb constructing, and so on. It’s not essential to ever really see the queen, as long as you see eggs or younger brood.
Colony Buildup
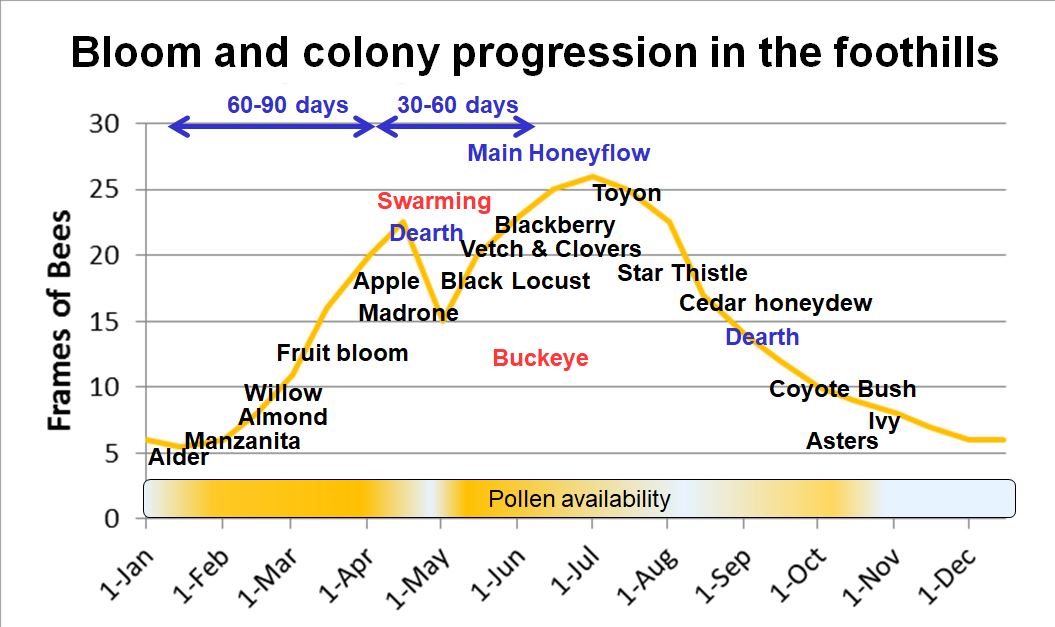
The first requirement for colonies to develop is loads of nutritious pollen (some pollens are extra nutritious than others). Colonies develop solely when pollen (and usually at the very least some nectar) is coming in. For my native space within the Sierra Foothills, pollen earnings and colony development are as beneath:
Word the everyday quantities of time required for an overwintered colony to construct as much as swarming, after which to its most inhabitants. And be aware how buildup follows pollen availability.
Administration in a Nutshell
Studying the Combs
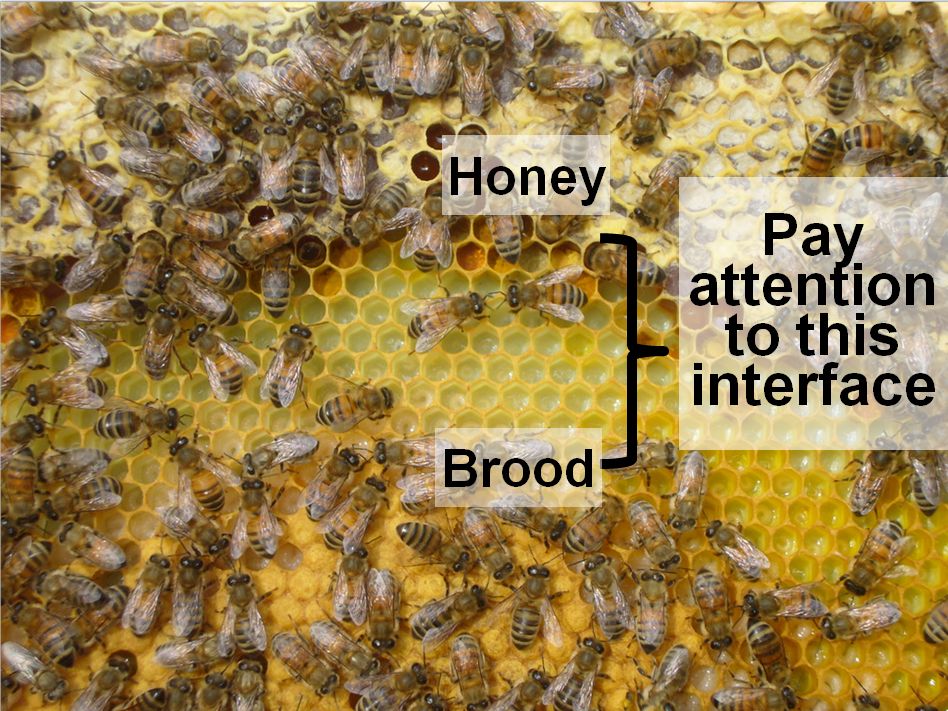
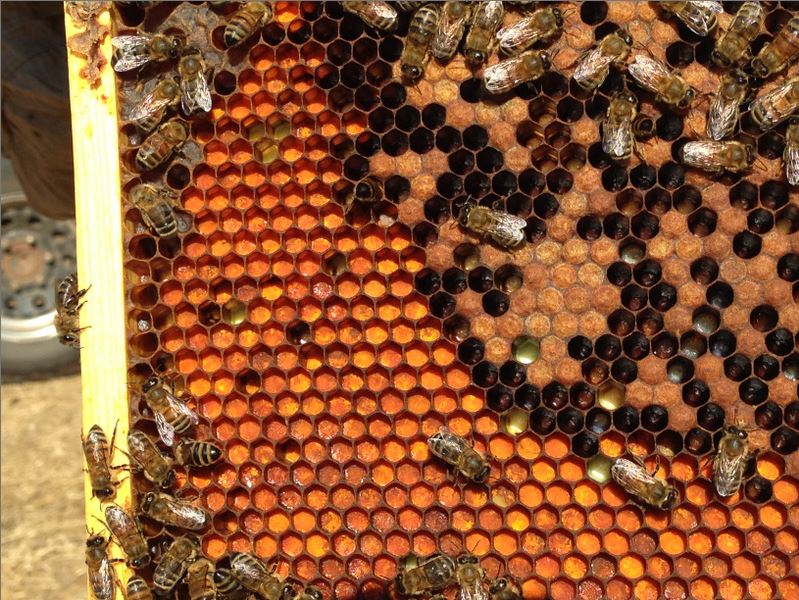
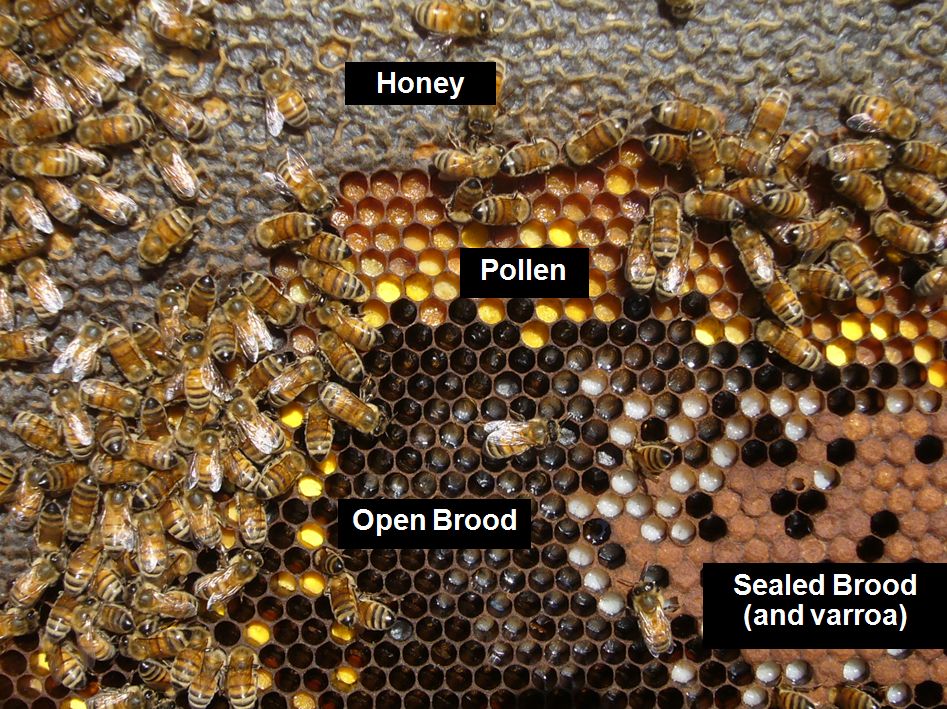
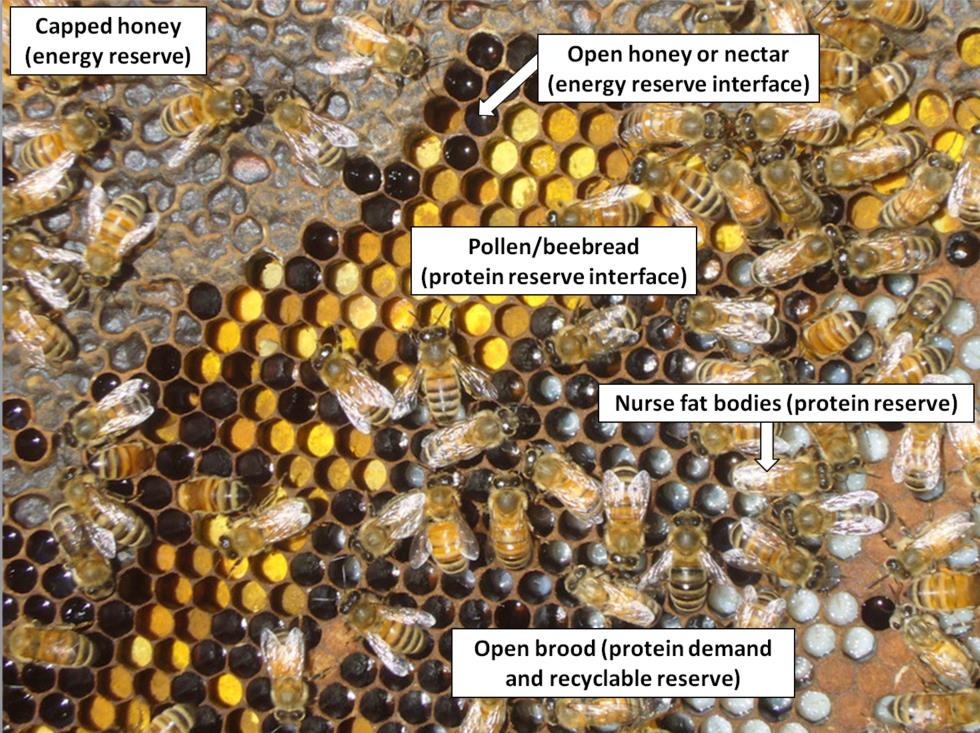
There may be little must ask others for recommendation–for those who be taught to learn the bees and the combs, the colony will inform you its precise situation, and no matter it wants. I’ve labeled the elements beneath.
To find out colony situation, work your option to a middle brood comb, and pay most consideration to the interface between the honey above, and the brood beneath.
On this dynamic interface, it is possible for you to to inform whether or not the colony is hungry or storing honey, and the way good their protein reserves are.
You all the time wish to see a pleasant band of beebread across the brood. Ought to this band disappear, suspect that the colony is affected by dietary stress (extra later). There isn’t a profit from feeding pollen sub patties to colonies if they’re already gathering loads of pure pollen (within the Foothills, sometimes from February by the tip of June, until there’s extended poor climate).
I’ve written a prolonged “Understanding Colony Buildup and Decline” sequence–all posted to ScientificBeekeeping.com. Studying this sequence from starting to finish offers you a deep understanding of the biology of this fascinating creature, and will let you make higher administration choices by yourself.
Preliminary Varroa Administration
Except I inform you in any other case, any nuc that I promote has already been handled to cut back varroa ranges (we use a dribble of oxalic acid syrup throughout a essential window of time; see Oxalic Remedy of Nucs). For packages, I counsel that you just give any bundle an analogous oxalic dribble therapy previous to Day 8 after set up (at which period varroa can start to “conceal” within the sealed brood). If the nuc has not been handled, I counsel the appliance of both a Hopguard II strip (thought of an “natural” therapy, however much less efficient), or an Apivar strip (artificial, however extremely efficient, since our mites haven’t beforehand been uncovered to amitraz).
Serving to the Colony to Develop
Because the inhabitants grows, and the colony can cowl extra frames, the bees will draw combs of basis from the middle out, and the queen will begin laying in these combs. That is your likelihood to observe a colony develop! (The inhabitants of bees in a nuc will broaden rapidly; that of a bundle, not till 3 weeks after set up).
Development of your colony will probably be dependent upon the native nectar and pollen flows.
The colony can’t increase extra bees with out pollen–pollen is the primary limiting issue for colony development and properly being. Colonies additionally want energy-rich nectar to warmth and fly, and for producing beeswax.
On the whole, pollen flows are satisfactory in most areas in spring, but when wet climate confines the foragers, the nuc will profit from being given a pollen sub patty or two (no profit if there’s pure pollen coming in). And until there’s a very heavy pure nectar circulation, the colony will vastly profit from being fed all of the 1:1 sugar syrup that they may eat (a half gallon a day if they may take it). Feed syrup till you see white wax being produced–they won’t draw comb until they’re producing white wax!
Making sugar syrup: use solely white granulated sugar (cane or beet). Sugars with any coloration might include undigestible carbohydrates or minerals which will trigger intestine dysbiosis. Feed “gentle syrup” for buildup (one half sugar to 1 half water, by weight or quantity); feed “heavy syrup” for placing on winter shops in fall (2 elements sugar to 1 half boiling water).
Study to acknowledge “white wax.” It is just when bees are producing white wax that they may construct comb and draw basis. It’s a signal to the beekeeper that the bees have crammed each accessible cell with nectar, and are crying for extra room. Thus, it’s an indicator of a robust nectar circulation, and a sign so as to add honey supers instantly.
Frequency of Inspection and association of combs
You might test the colony as usually as you want, however remember that clumsy dealing with by novices usually leads to queen loss–so deal with the combs fastidiously.
On the whole, place the combs again into the identical association that the bees had. All the time hold brood (and frames of eggs) collectively, honey to the surface, and pollen on the fringe of the brood nest.
Exception: It’s laborious for the bees to attract out the outermost combs of basis. As soon as the bees draw out the internal aspect of the second combs in, reverse these combs, and transfer them to the surface (provided that they include no eggs–see illustration).
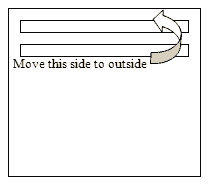
.
As soon as the combs have been drawn and crammed, their positions can normally be exchanged, simply be sure you hold brood combs collectively, and in the midst of the hive.
Dealing with tip: all the time run 10 frames in your brood chambers, squeezing them again tightly collectively after every inspection, after which centering them within the field.
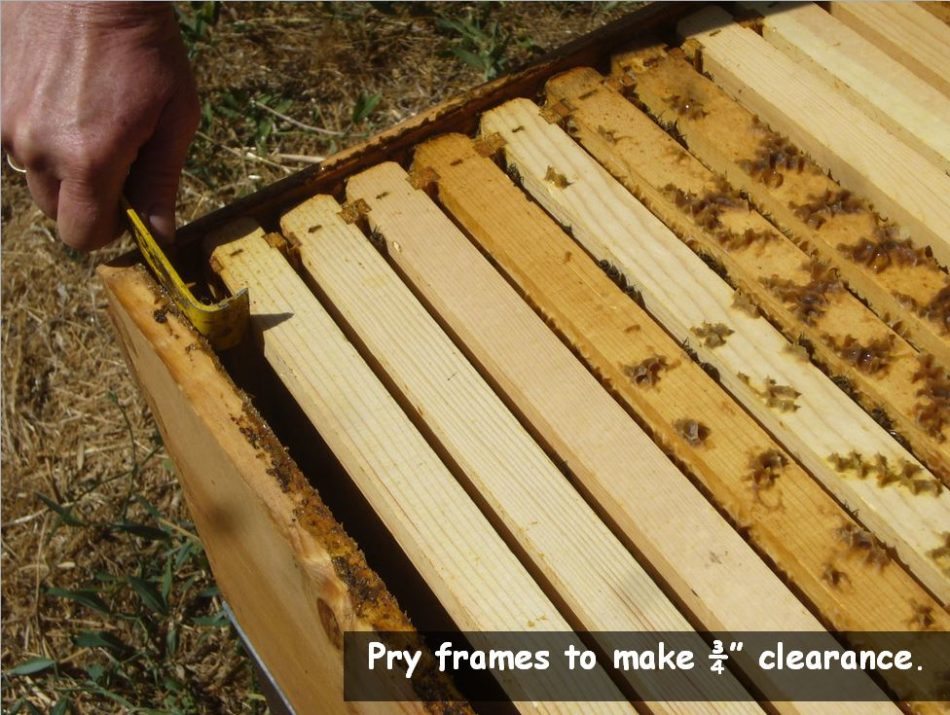
Stop propolis from build up between the tip bars–this may preserve correct bee area between the combs. All the time squeeze middle the frames tightly collectively, after which middle them within the field–you’ll be able to pry all of them sideways to go away 3/8″ inch clearance between the tip bars of the outer combs and the perimeters of the field. Should you all the time do that, you’ll typically get straight combs, and can all the time have working room between the combs.
Feed the colony sugar syrup repeatedly, however to not the extent that the queen is unable to broaden the brood nest as a consequence of extra saved syrup and nectar. If the bees retailer syrup within the middle of the brood space, reduce on feeding.
Word that there’s usually a big colony-to-colony variation in buildup and honey manufacturing. Except you will have different colonies to match to, it’s tough to know the way properly your colony is doing, in comparison with the “norm.”
Be sure to have a queen—indicated by eggs and brood of all ages. Word that it is not uncommon for novices to inadvertently kill the queen by inexpert dealing with of the frames!
Queen Points
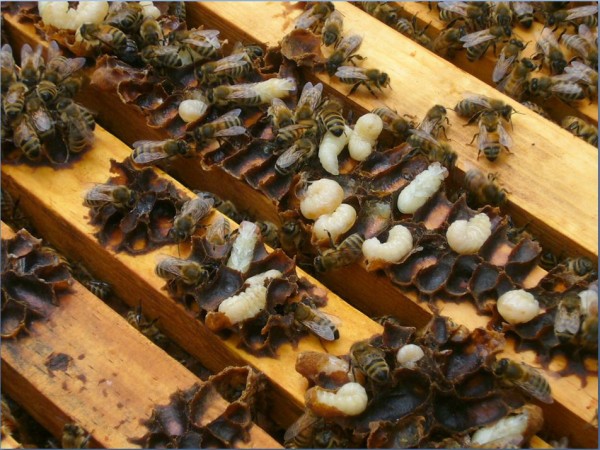
Examine to see that the queen is laying a daily sample of brood in concentric rings by age. If brood sample is spotty or uneven, the queen might have an issue, or the colony could also be affected by a brood illness.
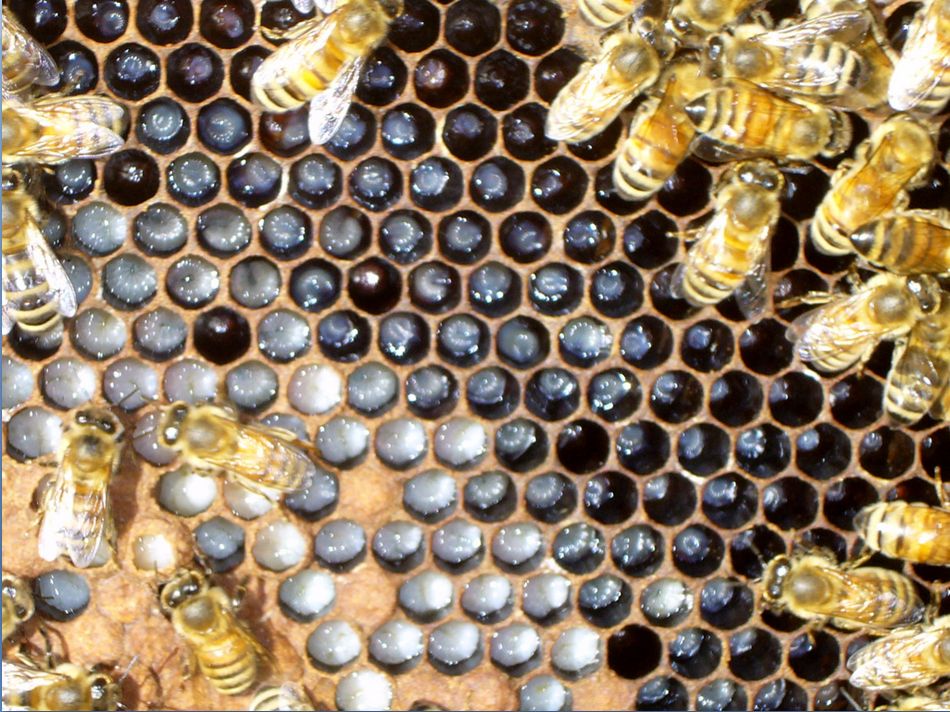
Above, a colony with well-fed, wholesome brood. Word the even stepwise development of larval ages,their excessive charge of survival, and the copious jelly being fed to the younger larvae–all indicators of a superb queen in a colony in good well being, having fun with good forage situations.
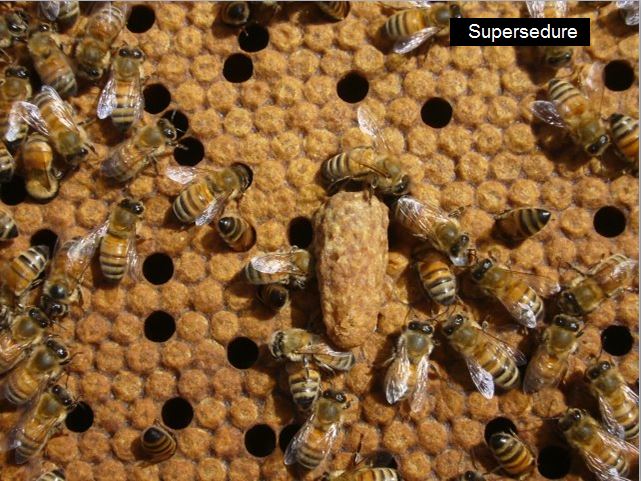
It’s well-known that in people, the females enhance with age. Not so with honey bee queens. As soon as a queen has mated, her provide of saved spermatozoa is finite, and sometimes begins to run quick after two seasons of broodrearing in a big colony (she’ll last more the place seasons are quick, or in a small colony). This depletion sometimes happens within the late summer season of their second season. At this level, a number of the eggs that she lays in employee cells might not get fertilized, and the queen turns into a “drone layer” (photograph beneath). In nature, the bees sometimes substitute their queen when this happens by way of a course of known as supersedure.
(Above) indicators of a failing queen. Unfertilized eggs laid in employee cells (leading to scattered drone brood), and a supersedure queen cup close to the highest of the photograph. Time to exchange the queen!
Colonies substitute their queen by producing a number of supersedure cells, sometimes on a comb face. Enable them to take action. The mom and her daughter might coexist fortunately collectively within the hive for a while.
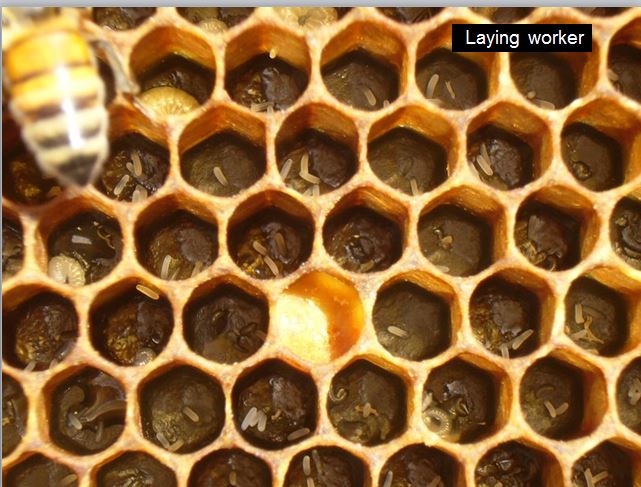
If there are a number of scattered eggs in a cell, otherwise you see bullet-shaped cappings in employee brood cells, the colony could also be “hopelessly queenless” with “laying employees.” Such colonies sometimes exhibit a “queenless roar” when smoked, their wings are all jittery when disturbed, and the employees get pissy. Laying employee colonies are tough to requeen–it’s best to mix them with a queenright colony–simply set them proper on prime.
Queen cells
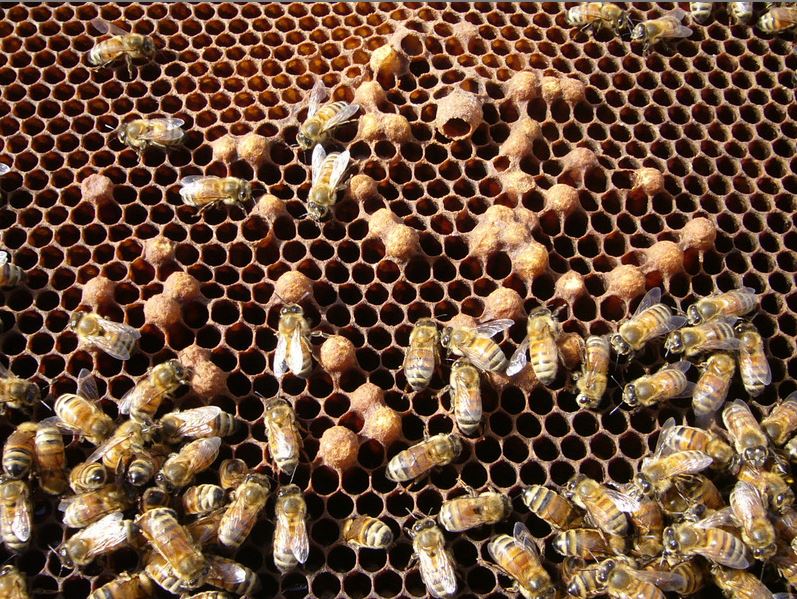
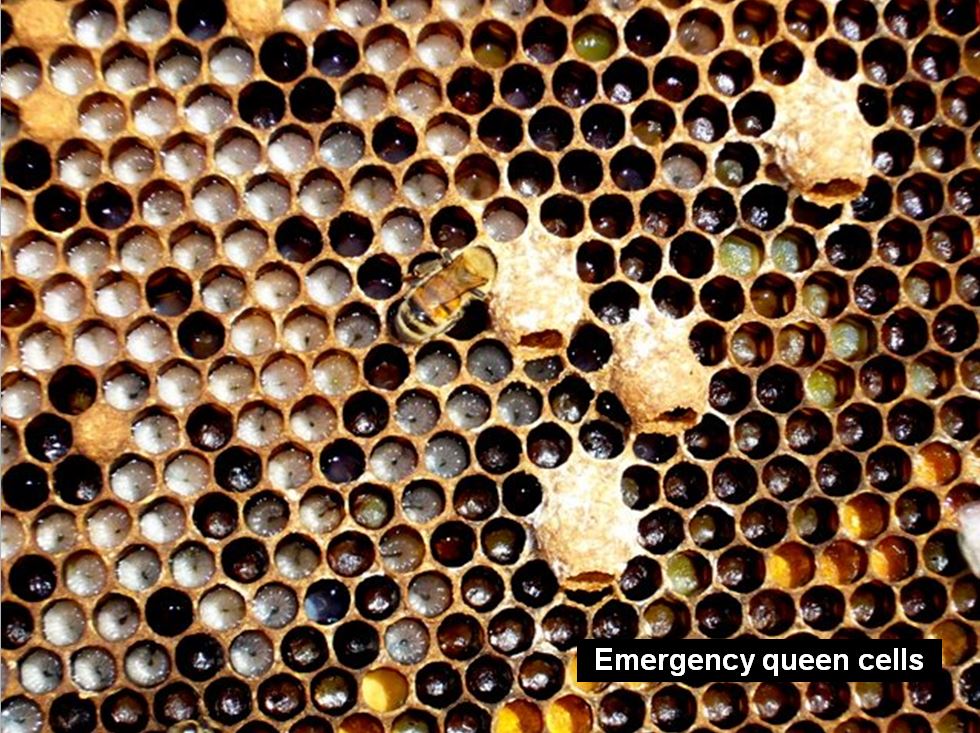
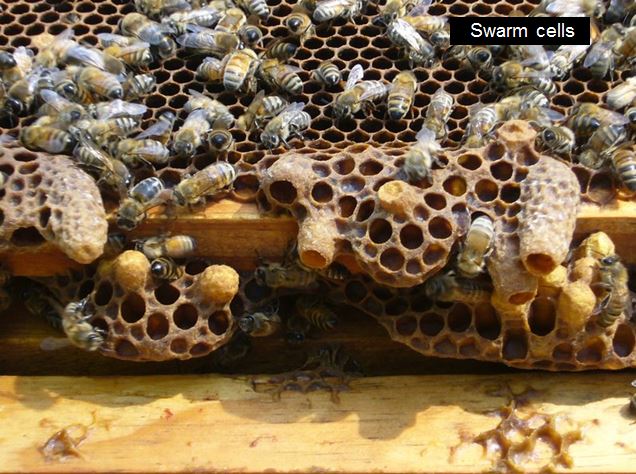
If there are queen cells being fashioned, the colony might have misplaced their queen (you’ll see a number of small, scattered emergency queen cells), could also be superseding the queen (one or two very massive queen cells on the aspect of a body; permit the method to proceed), or be making ready to swarm (massive queen cells usually on the backside of the frames–colony wants extra room).
Should you see emergency queen cells with a larva and jelly inside, you will have seemingly misplaced the queen–both requeen or permit the colony 25 days to requeen itself. Smaller “queen cups” with out eggs or jelly inside or regular.
Within the springtime, a crowded colony (not given sufficient area) will construct swarm cells on the bottoms of the combs. Within the above photograph, there’s one queen cup, two beginning swarm cells, one practically full cell, and one sealed swarm cell. Queen cells are all the time vertically oriented– the opposite massive horizontal cells are regular drone cells.
Requeening
There are just a few methods to requeen your colony. You possibly can permit the bees to do it themselves by way of supersedure, however that is dangerous within the foothills because of the restricted provide of drones in late summer season, maybe leading to a poorly-mated new queen going into winter.
You possibly can rear your personal daughters out of your favourite queen by merely creating just a few nucs in springtime, and permitting every to rear emergency queen cells. It would take a minimal of 24 days earlier than the brand new queen begins laying eggs.
You possibly can pace up the method by buying or grafting queen cells–see Queens for Pennies.
Regardless of claims, makes an attempt to requeen a queenright colony by putting a queen cell into it are typically unsuccessful–you should take away the previous queen first. I typically choose to introduce my queen cells into nucs for mating out, after which after seeing the brand new queen’s brood sample, then introduce the nuc right into a colony that has sat for a day after eradicating its queen. Gently place the nuc right into a full-sized brood chamber, take away the quilt from the colony to be requeened (no queen excluder), lay a strip of newspaper at the very least as vast because the nuc lengthwise excessive bars (this prevents the brand new queen from working downhill into overseas bees), and place the quilt excessive. After just a few days, you’ll be able to rearrange the combs.
If as a substitute you buy a caged queen, if she’s been banked, she might have to be fed by the bees for a day to get her into laying situation and to choose up the colony odor for higher acceptance. A great way to make sure that your caged queen will probably be accepted is to do a two-step course of:
- First, queen acceptance is greatest when there’s a nectar circulation on and no robbing–it could assist to feed the colony syrup. Additionally, queens are extra readily accepted by younger bees with brood–in case your colony has been queenless for a while, it could assist so as to add a body of younger brood with the adhering nurse bees. And in any case, you’ll typically get greatest acceptance right into a newly-made nuc that has sat queenless for a day or two.
- Press the queen in her cage, within the brood space, with the display screen of the cage absolutely uncovered to the bees, into the comb (keep away from comb with honey, as you’ll be able to drown the queen). Maintain the sweet coated with the cork or cap, or vinyl tape. Wait 24 hours. After 24 hours gently open the hive with minimal smoke and examine the habits of the bees on the cage. If they’re strolling evenly over the display screen as beneath, and you’ll see them providing the queen meals, and the bees will be moved with a mild contact of your finger, they’ve accepted the queen. You possibly can then expose the sweet, substitute the cage, and permit the bees to chew by the sweet to launch her after you’ve put the hive again collectively.
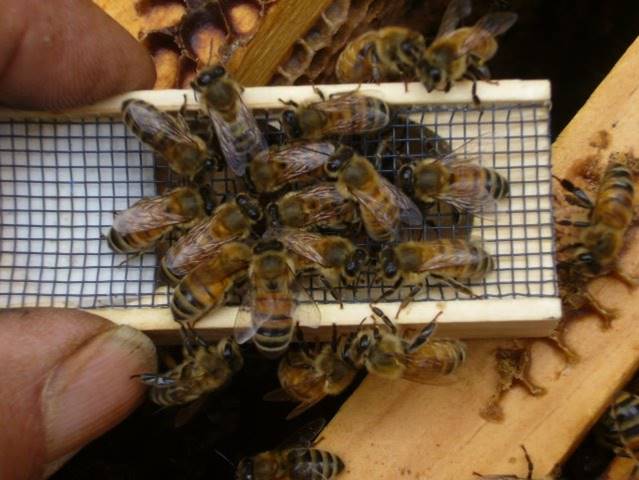 Within the photograph above, the bees have accepted the queen. Within the photograph beneath, they haven’t, and are trying to “ball” the queen and cook dinner her. The bees beneath are behaving aggressively in direction of the queen, and won’t transfer whenever you contact them.
Within the photograph above, the bees have accepted the queen. Within the photograph beneath, they haven’t, and are trying to “ball” the queen and cook dinner her. The bees beneath are behaving aggressively in direction of the queen, and won’t transfer whenever you contact them.
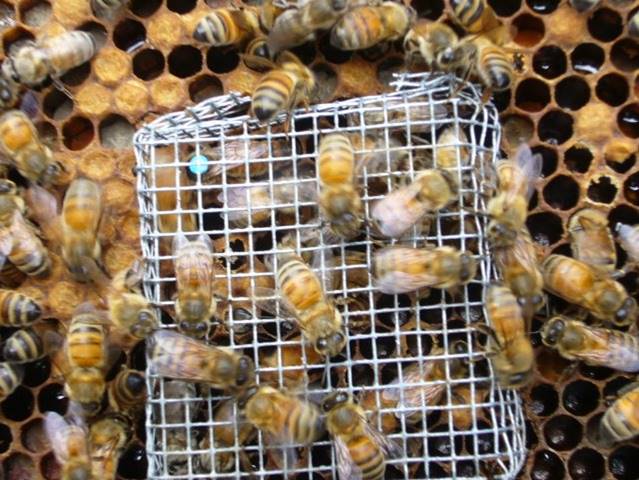
 Within the case above, you probably have a free queen remaining within the hive (or maybe she wants one other day)–no sense to launch the brand new queen, as she’ll be killed. It is advisable to both discover the opposite queen, or introduce the queen right into a queenless nuc.
Within the case above, you probably have a free queen remaining within the hive (or maybe she wants one other day)–no sense to launch the brand new queen, as she’ll be killed. It is advisable to both discover the opposite queen, or introduce the queen right into a queenless nuc.
One other methodology that works properly is to make a “press in cage” of 1/8″ {hardware} fabric (washed to take away any oil). Place the cage over some rising brood, tip it up and punctiliously launch the caged queen into the display screen cage, and gently press the display screen pretty deep into the comb. Then open the hive after a few days and if all seems to be properly, gently launch the queen–watching to make it possible for the bees don’t assault her.
 A tip: new beekeepers usually handle to permit a caged queen to fly off. Should you achieve this, freeze, and she is going to usually return to the cage in a couple of minutes. Stop this from occurring by dealing with caged queens in a closed room, your automotive, or in your eliminated veil.
A tip: new beekeepers usually handle to permit a caged queen to fly off. Should you achieve this, freeze, and she is going to usually return to the cage in a couple of minutes. Stop this from occurring by dealing with caged queens in a closed room, your automotive, or in your eliminated veil.
Issues and Ailments
Hive Invaders
Bears
Should you stay the place there are bears, you’ll want to guard your hives from them. Bears are surprisingly robust, however will be deterred by a well-constructed electrical fence. For the fence design that we use efficiently within the Sierra Foothills, see Bear Fence Directions.
Skunks
Skunks might scratch on the hive entrances at evening. This may be prevented by nailing carpet tack strips throughout the doorway, or if the hive is on the bottom, merely sprinkle a teaspoon of lye crystals onto the scratched floor, the skunks don’t just like the style, and will be simply skilled to cease bothering the hive. Racoons don’t hassle hives with stay bees in them.
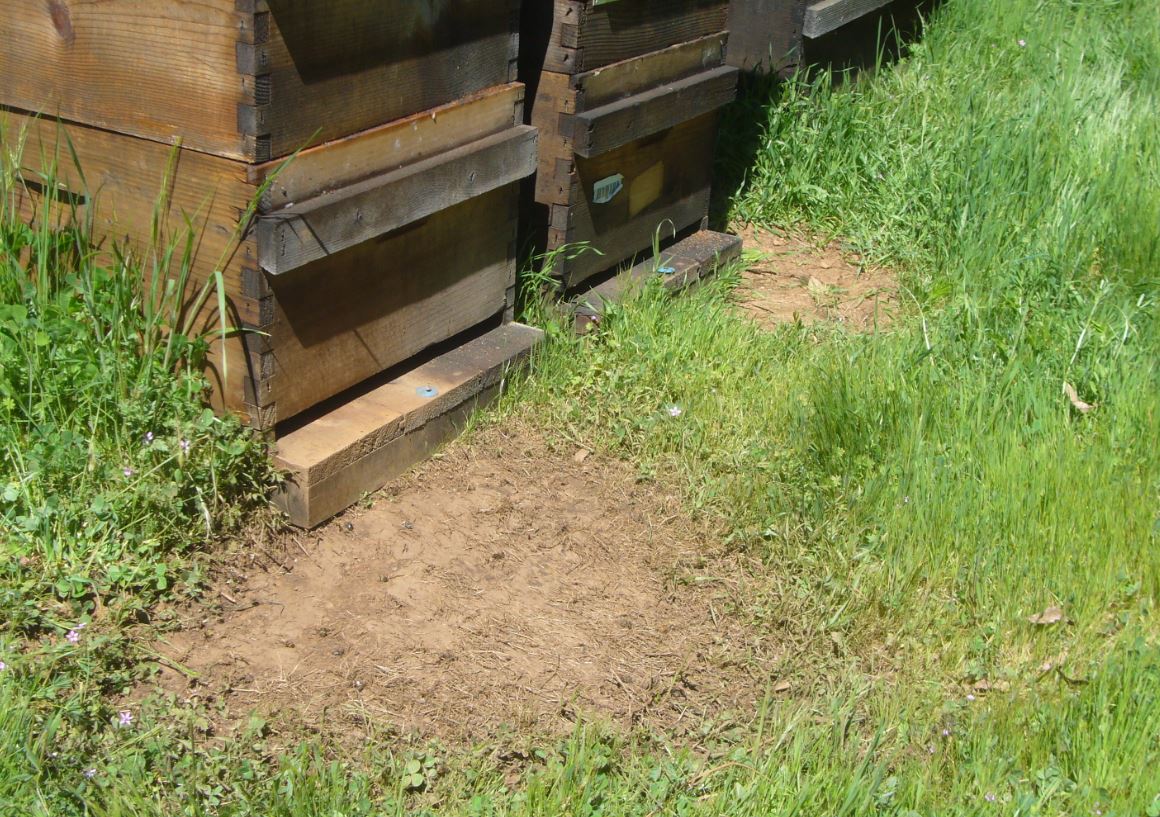 Indicators of skunk scratching. We don’t wish to hurt our skunks, so as a substitute practice them with an sprinkling of lye crystals on the scratched floor.
Indicators of skunk scratching. We don’t wish to hurt our skunks, so as a substitute practice them with an sprinkling of lye crystals on the scratched floor.
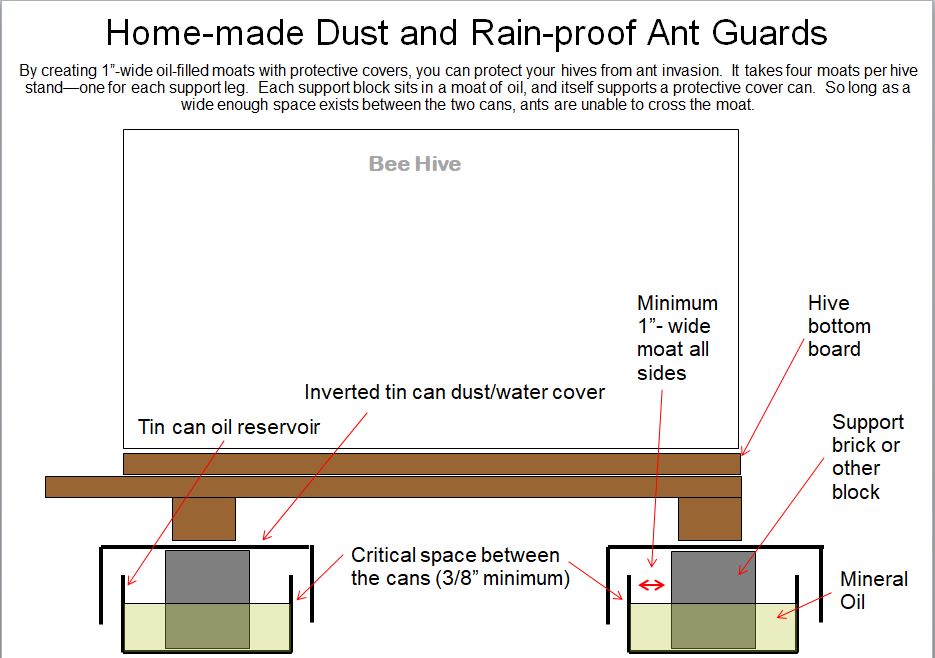
Ant Management
Ants could also be problematic in some areas. It’s frequent to seek out ants nesting between the outer and internal cowl, or across the hive. However there are only some ant species that can really invade a hive. In California, Argentine ants is usually a significant issue. I’ve no expertise with ant species present in different states.
It’s greatest to not spray or unfold pesticides close to the hive, since ants are intently associated to bees, and are prone to the identical pesticides!
You will have two choices:
1. Poison the ants. For precise long-term success, you need to use a bait that the ants will carry again to their colony and kill the queen. For that goal, borax or fipronil work greatest.
Since most invasive ants are in search of sugar, a sugar bait similar to Terro, or home made bait of 5% borax (sodium tetraborate) in honey or sugar syrup, provided in a Mason jar with 1/8″ display screen within the lid works properly. Fipronil-based ant bait stations are additionally very efficient at killing an ant colony, however make sure that your bees can’t acquire entry to the bait.
2. Shield the hive by putting it on a stand which ants are unable to traverse.
I lately seen some fairly cool ant stands being bought by a small California firm: https://defyantstands.com/
Word, combs and containers from diseased or “deadout” hives will be reused with out sterilization, apart from AFB.
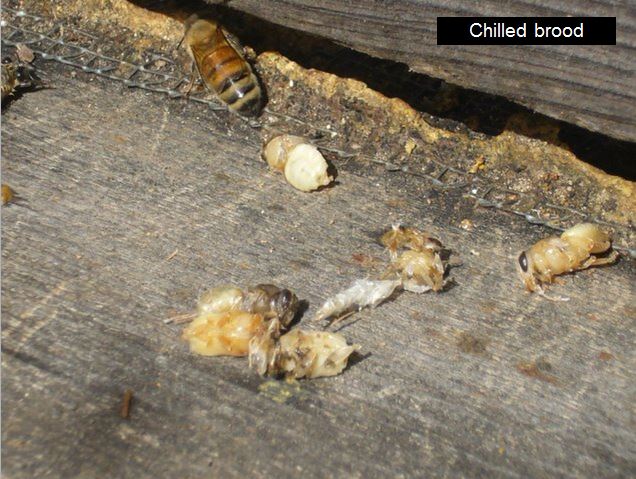
Chilled Brood
An sudden chilly evening within the spring can lead to some chilling of the brood on the periphery of the cluster. You might even see pulled out pupae on the touchdown board the following morning. You do not want to take any motion.
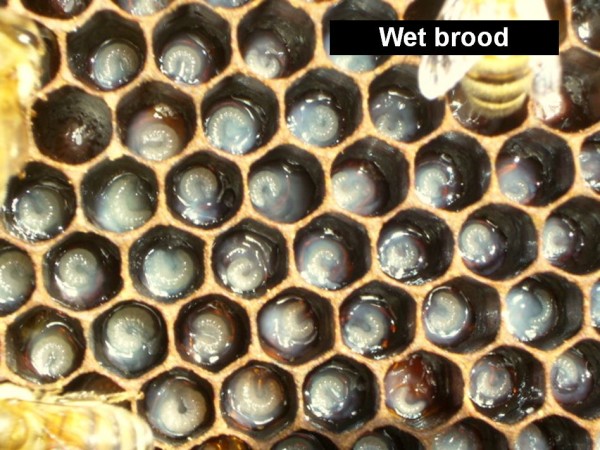
If the brood is “spotty,” search for indicators of brood illness—chalkbrood (white & tan “mummies”), EFB (twisted white & yellow larvae–usually laborious to diagnose), or AFB (sunken perforated cappings, melted brown larvae that “rope”).
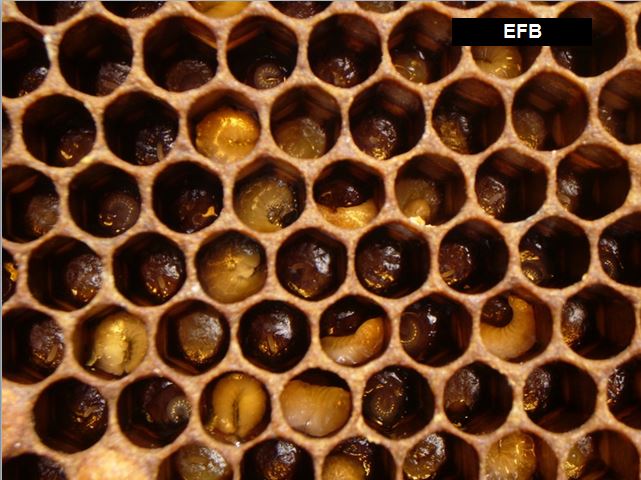
EFB
EFB is a typical bacterial illness, particularly in careworn colonies within the spring.
European Foulbrood (EFB) above. EFB used to simply “go away” by itself; our present pressure doesn’t. Deal with with oxytetracycline — a pure antibiotic. Oxytet now requires a veterinary prescription, however any skilled beekeeper will seemingly have some available.
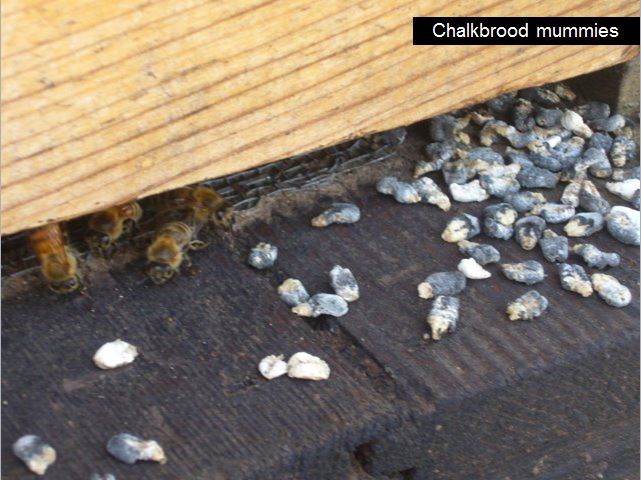
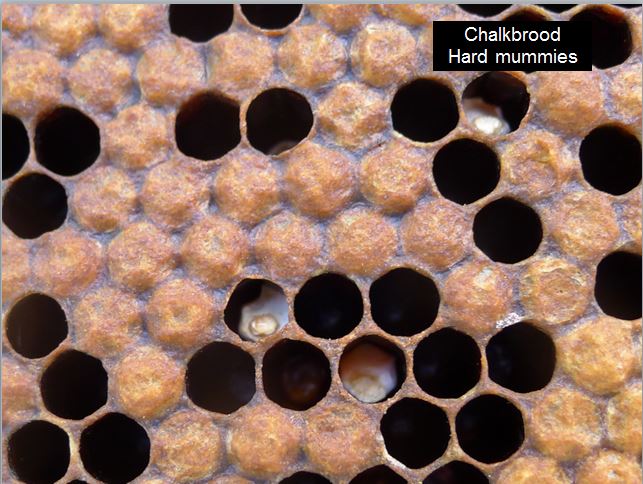
Chalkbrood
One other brood illness is Chalkbrood (a fungal illness):
Chalkbrood produces distinctive, two-toned laborious “mummies” within the combs.
There isn’t a therapy for chalkbrood. If it doesn’t spontaneously disappear, one of the best recommendation is to requeen the hive.
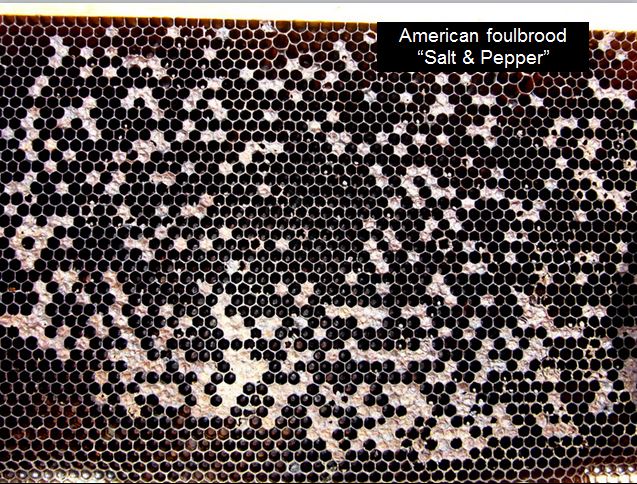
AFB
Essentially the most severe illness (apart from varroa-induced virus collapse) is American Foulbrood (AFB)–a extremely contagious bacterium that may unfold to your neighbors’ hives. Though AFB is now unusual in skilled apiaries, it’s presently resurging in some city areas which have a whole lot of interest beekeepers who don’t acknowledge this significant issue.
AFB is nothing to mess with–ask for assist for those who suspect that you just see it, after which scrupulously eradicate it earlier than it unfold to your neighbors!
AFB produces a particular, “salt and pepper” brood sample, with some cells having sunken, perforated cappings. It typically has a robust distinctive disagreeable odor (a cross between fitness center socks and lifeless rotting bees).
The caramel-colored melted pupae (above) are distinctive for AFB. Stir a dry stick into the melted brood cell after which slowly withdraw it. If the slime ropes out for 3/4″, that’s diagnostic of AFB. We burn colonies if we see even one cell! Don’t ignore AFB!!!!
Colonies which have died from AFB can have black “scales” tightly adhered to the underside of the brood cells. If shopping for or reusing combs, test them fastidiously for AFB scales, as it is a frequent option to unfold the illness.
AFB combs should be burned or safely disposed of in a landfill. The containers will be sterilized and reused.
The Clear Up Crew
As soon as a colony weakens or dies, if the climate is heat, the Wax Moth will transfer in and lay eggs. Its caterpillars will quickly eat any pollen shops, boring by the combs, and constructing silken tubes and webbing, and chewing into the wooden to pupate. You possibly can take away the silk (particularly the white cocoons), and reuse the frames with no extra cleansing.
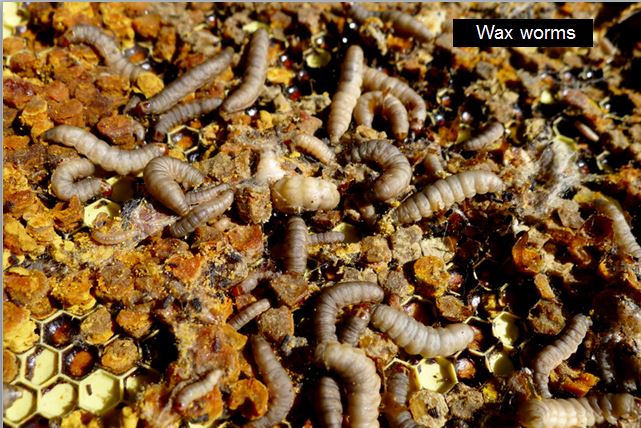

Wax moth is usually solely an issue when temperatures are above about 70°F. Retailer containers of darkish combs with gentle and air publicity (by no means wrapped up or stacked) to keep away from wax moth injury. BTW, wax worms make nice pet meals, and are tasty to eat, uncooked or cooked.
OK, most of you gained’t have any of the issues above, and your nuc or bundle will quickly outgrow their first brood chamber.
Including the Second Brood Chamber
As soon as the bees of your colony cowl all 10 combs within the first brood chamber, it’s time to add a second brood chamber of basis above it. At this level of time, it is best to assess the varroa infestation degree in your colony. I’ll return to including your second brood chamber after I talk about varroa administration.
Varroa Mite Administration
Varroa is the Main Explanation for Colony Morbidity and Mortality
The main reason behind colony failure for novices is from not managing varroa mite ranges, which then permits viruses and nosema to kill the colony.
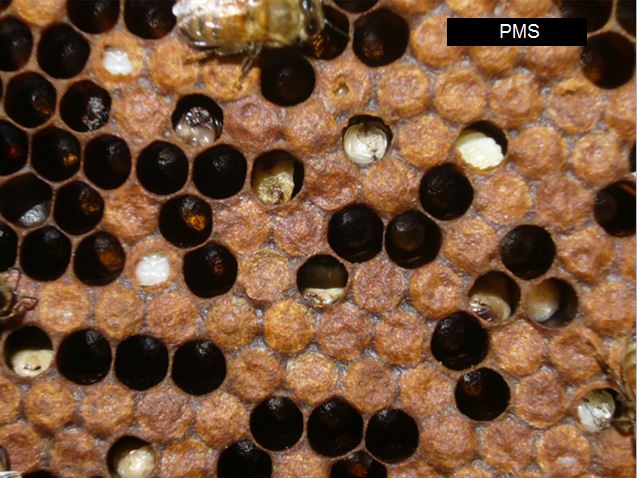
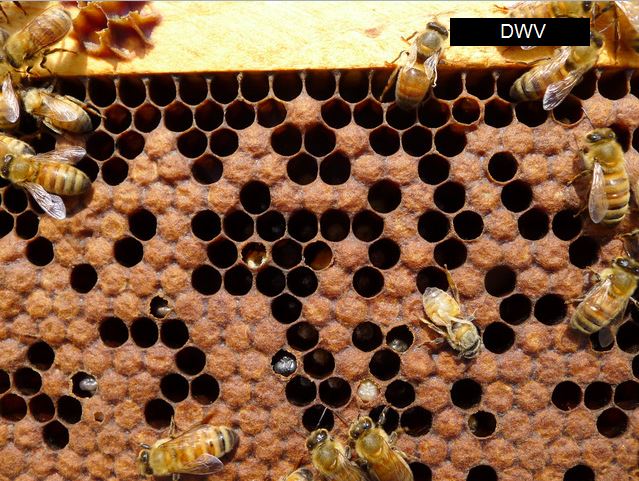
The varroa mite transmits viruses (primarily Deformed Wing Virus) inside the hive, leading to dying brood. That is known as Parasitic Mite Syndrome (PMS). As soon as a colony reaches this stage (above), it’s tough to save lots of.
Word the 2 bees with deformed wings within the photograph above–they’re affected by varroa-transmitted DWV. Additionally be aware the dying brood, and bees unable to emerge.
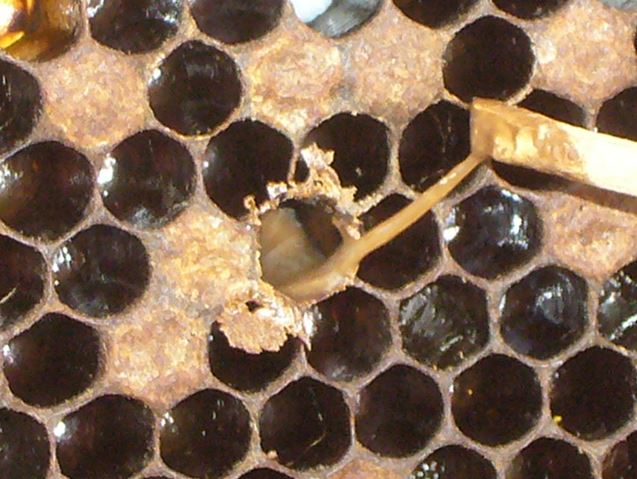
In case your colony was robust in summer season, after which the bees immediately disappear in fall, abandoning loads of honey above, and scattered sealed brood within the decrease field, varroa is usually the perpetrator. You possibly can diagnose by holding a brood body horizontal with the highest bar away from you. With the solar coming over your shoulder to light up the “ceilings” of the cells, search for the telltale white guanine deposits left by mites. Should you see them, it was almost definitely varroa that did your colony in. Listed here are some pictures of typical varroa deadouts:
 On this photograph I’ve the highest bar towards me (solar to my again), wanting on the “flooring” of the cells for AFB scale. To search for guanine deposits from varroa, flip the highest bar away from you.
On this photograph I’ve the highest bar towards me (solar to my again), wanting on the “flooring” of the cells for AFB scale. To search for guanine deposits from varroa, flip the highest bar away from you.
Tip: when inspecting combs, search for the shadow of your head on the bottom, after which face it. This may put the solar immediately behind your again (with out blinding your self by wanting immediately on the solar).
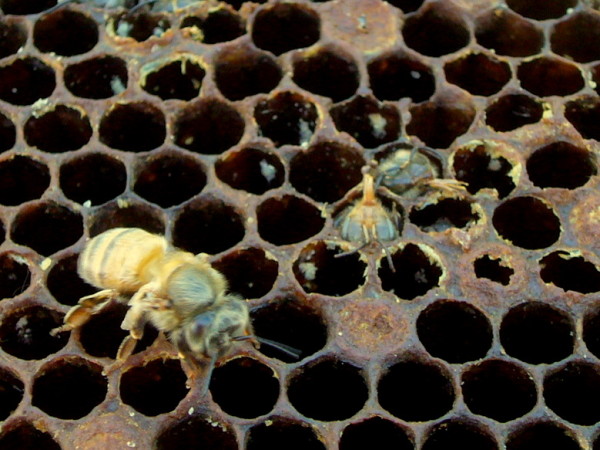 A colony dying from varroa/DWV. Word the deformed wings on the bee, and the fully-formed adults within the cells unable to emerge–a typical signal. Word the white guanine deposits left by the mites on the cell “ceilings.”
A colony dying from varroa/DWV. Word the deformed wings on the bee, and the fully-formed adults within the cells unable to emerge–a typical signal. Word the white guanine deposits left by the mites on the cell “ceilings.”
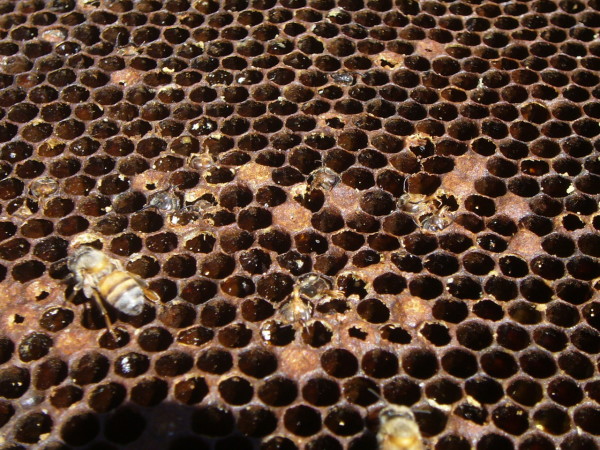 One other shot of a colony dying from varroa/DWV. Once more, be aware the white deposits.
One other shot of a colony dying from varroa/DWV. Once more, be aware the white deposits.
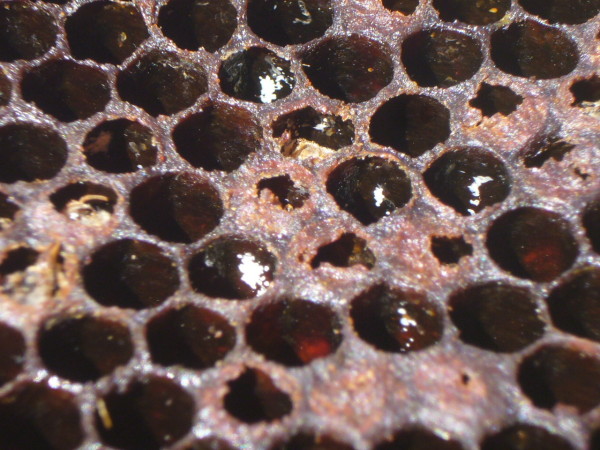 Shut up of some guanine deposits, some grownup brood unable to emerge, and a few cells with the cappings partially chewed open. All typical of a varroa kill.
Shut up of some guanine deposits, some grownup brood unable to emerge, and a few cells with the cappings partially chewed open. All typical of a varroa kill.
“Remedy Free” Beekeeping
Though my aim is to develop a inventory of bees that require no therapy for varroa, I adamantly do not suggest “treatment-free” beekeeping for novices. It’s biologically and ethically unjustified, inexcusable so far as working towards good animal husbandry, and spreads mites and viruses to your neighboring beekeepers and any struggling populations of feral honey bees, and viruses to native pollinators.
Management varroa, or colonies will typically die an unsightly and pointless loss of life from the varroa/virus advanced. Not solely that, however when that colony crashes, it floods the encircling colonies with varroa mites, making you a nuisance to each surrounding beekeepers, and the feral inhabitants of bees that’s slowly evolving resistance to the mite. PLEASE MANAGE MITE LEVELS IN YOUR HIVES AND DO NOT ALLOW COLONIES TO COLLAPSE FROM VARROA.
When you’ve mastered maintaining colonies alive and wholesome for at the very least three years, then you’ll be able to experiment with going with out mite therapies (don’t anticipate most industrial bee shares to outlive with out therapy–you’ll seemingly have higher luck with VSH, Russian, or feral survivors). There are a number of easy-to-use and efficient “pure” mite therapies available on the market that won’t contaminate your combs or honey, in addition to biotechnical strategies similar to drone brood trapping and queen caging.
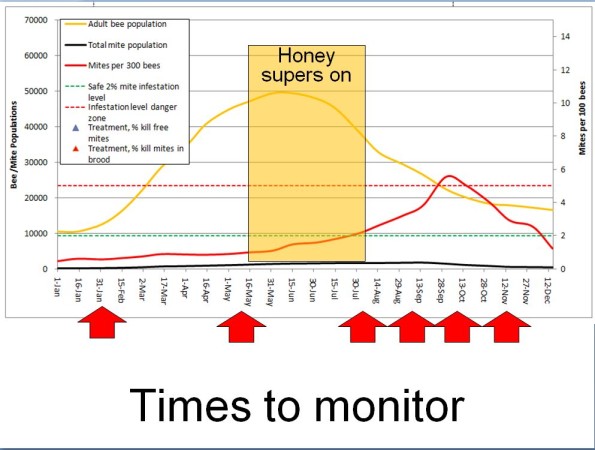
Monitoring Varroa Infestation Ranges
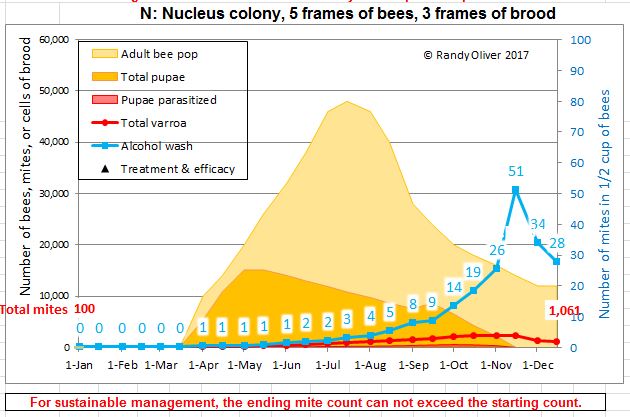
Each bee colony accommodates varroa mites, and extra drift in from different hives. And though we breed for resistant inventory, the overwhelming majority of our hives require mite therapies to outlive. Mite buildup follows a predictable development curve. My mite mannequin demonstrates the anticipated mite inhabitants and alcohol wash counts for a nuc, handled earlier than buy:
The graph above is from Randy’s Varroa Mannequin — a free obtain that runs on Excel https://scientificbeekeeping.com/randys-varroa-model/
Within the above chart, the nuc began with an inexpensive 100 mites in April. Word the development of alcohol wash counts. This nuc had an opportunity to outlive the winter, however would begin the following season with far too many mites to outlive a second yr. Word: the alcohol wash mite counts rise considerably extra slowly than the precise mite inhabitants–notice that the mite wash depend will rise quickly in late summer season because the colony bee
inhabitants begins to say no. You wish to be proactive fairly than reactive with mite administration–intervene in early July if mite counts exceed 4 mites!
Examine to the chart beneath, with a considerably 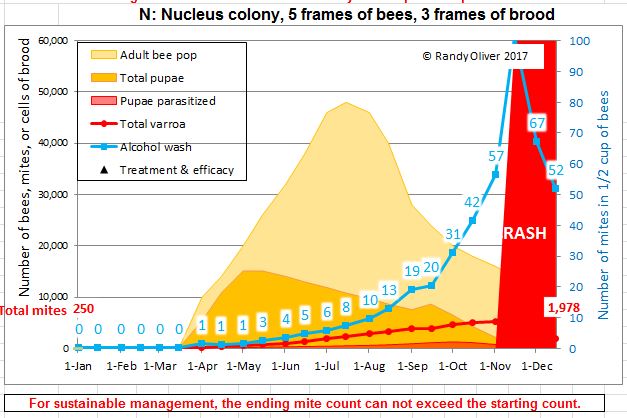
Within the above chart, I began with 250 mites in April. Word that the beginning alcohol was depend was nonetheless low, however the colony crashed in November. Had the hive been in an space the place there have been different high-mite hives, it might have crashed even earlier, as a consequence of mite immigration out of your neighbors.
Sensible suggestion:
Except you’re a breeder, there’s little purpose to attend till monitoring suggests that you just’ve reached an motion threshold.
As an alternative, use spot-monitoring of 300-bee samples (by detergent wash) to verify that you just’re sustaining satisfactory mite suppression in your operation.
In case your counts are all the time zeroes, you’ll be able to seemingly again off a bit in your therapy schedule.
If as a substitute, counts begin to exceed 6 mites, modify your therapy schedule.
That is particularly vital in late summer season if there’s a lot mite drift in your space.
Anticipate mite counts to leap a bit when the colonies wind down brood rearing in fall (or throughout dearth) — affirm by monitoring that your therapy schedule takes benefit of hitting the mites when they’re all out of the brood (we choose OA dribble or extended-release).
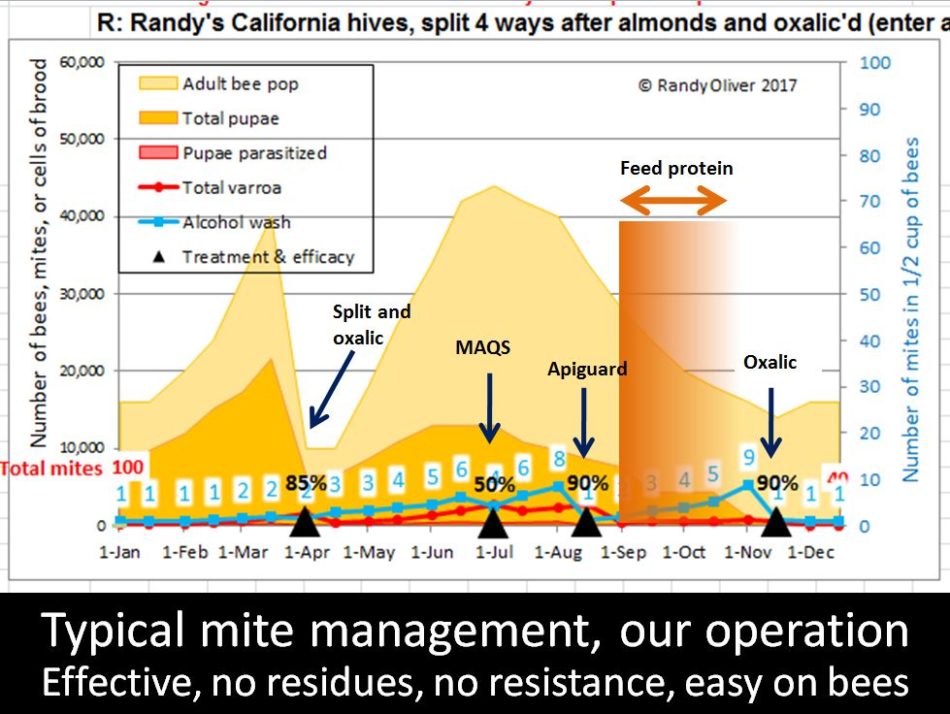
Right here within the California foothills, with 11 months of broodrearing, most colonies would require three or 4 95% reductions of their mite ranges in the course of the season.
Beginning in July after putting in a brand new nuc or bundle, it is best to take a look at it for mite degree, utilizing a sticky board or different methodology (I strongly suggest the “alcohol wash” or “sugar shake”). Assume that each one nucs have varroa mite. You will need to monitor mite degree, and deal with if the mite degree exceeds the seasonal “therapy threshold” (3 mites/half cup of bees previous to July 1, 6 mites from July 1 by late fall). We’re having nice success with mite-tolerant queens, biotechnical strategies, and “pure” therapies.
I like to recommend mite testing in early spring, earlier than supering, once more in early August, and in late September (Northern Calif).
Because of the big variability of stickyboard counts, any single stickyboard depend is sort of meaningless. Nevertheless, they are often of use if executed recurrently.
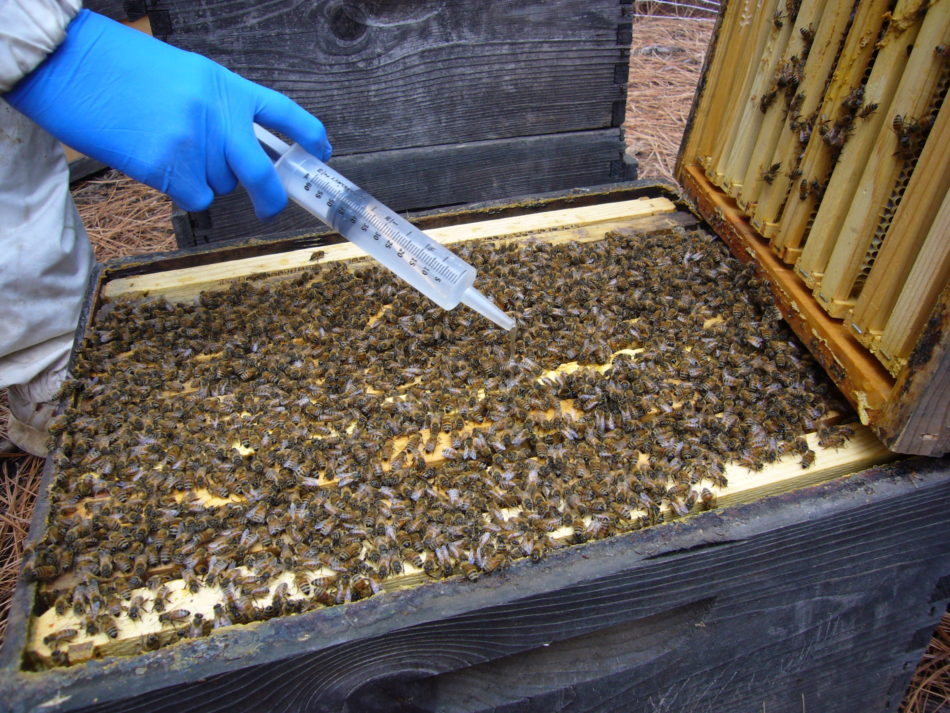
The perfect take a look at is an alcohol or detergent wash of a degree half cup of bees (~320 bees), or the “sugar shake” (see https://scientificbeekeeping.com/sick-bees-part-11-mite-monitoring-methods/)–I like to recommend the alcohol wash over the sugar shake. Studying to do an alcohol wash is so vital, that I’m going to enter element as to the best way to do it!
Replace August 2020: We have now switched from utilizing alcohol to Daybreak Extremely dishwashing liquid, diluted to 2 Tablespoons per gallon. Enable the bees to soak within the detergent for 1 minute previous to a swirl agitation. Because of the foam, then depend the mites wanting up from the underside of the cup — a 10X make-up magnifying mirror helps.

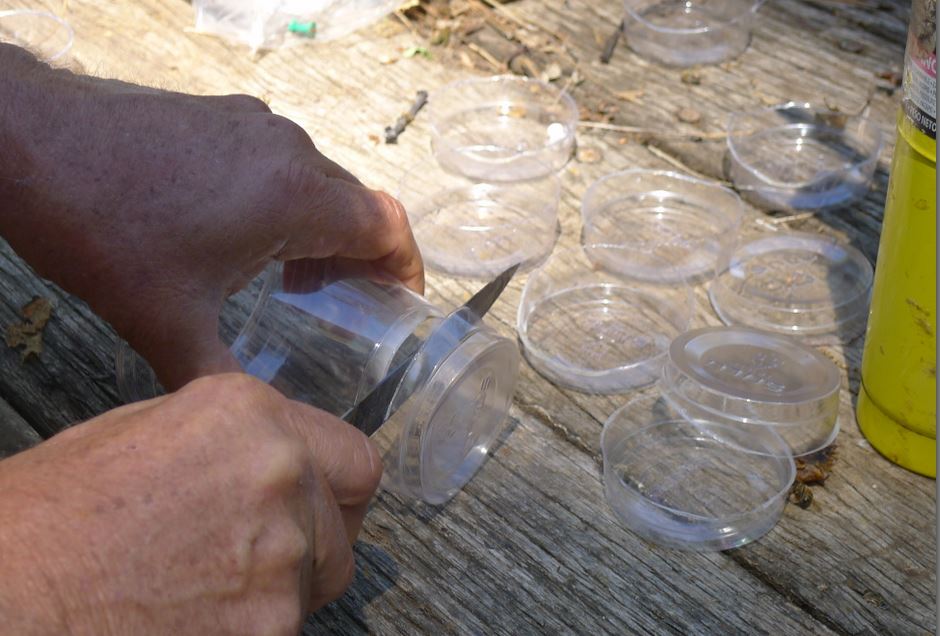
First, construct a mite wash cup set. For particulars, see these hyperlinks: An Improved mite washer and Nonetheless bettering.
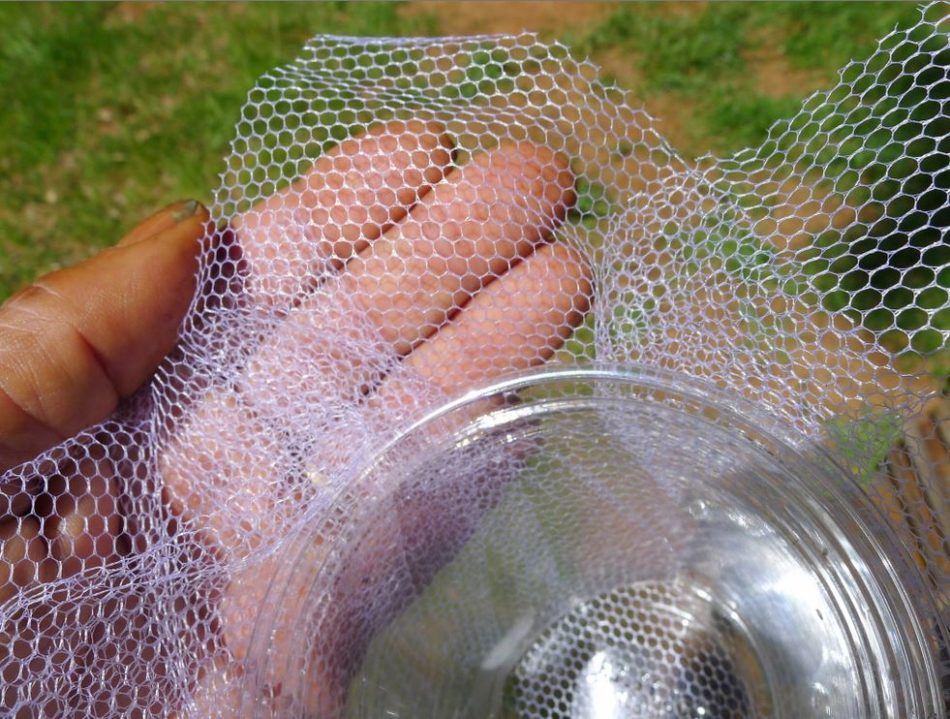
The only is constructed from two clear 16-oz plastic cups with a snap-on lid, plus a bit of mesh material. Use a heated knife blade to chop roughly 1/2-3/4″ off the underside of 1 cup, leaving a easy edge:
Then reduce a 12″ sq. of “mesh” or “Tulle” material–not the opening measurement, which should be massive sufficient for the pinhead-sized mites to cross by.
The reduce cup goes into the uncut cup, with the mesh between them:
We hate to see the bees that we promote die from neglect, and are blissful to present you a ready mite wash cup as above any time–simply ask whenever you come by.
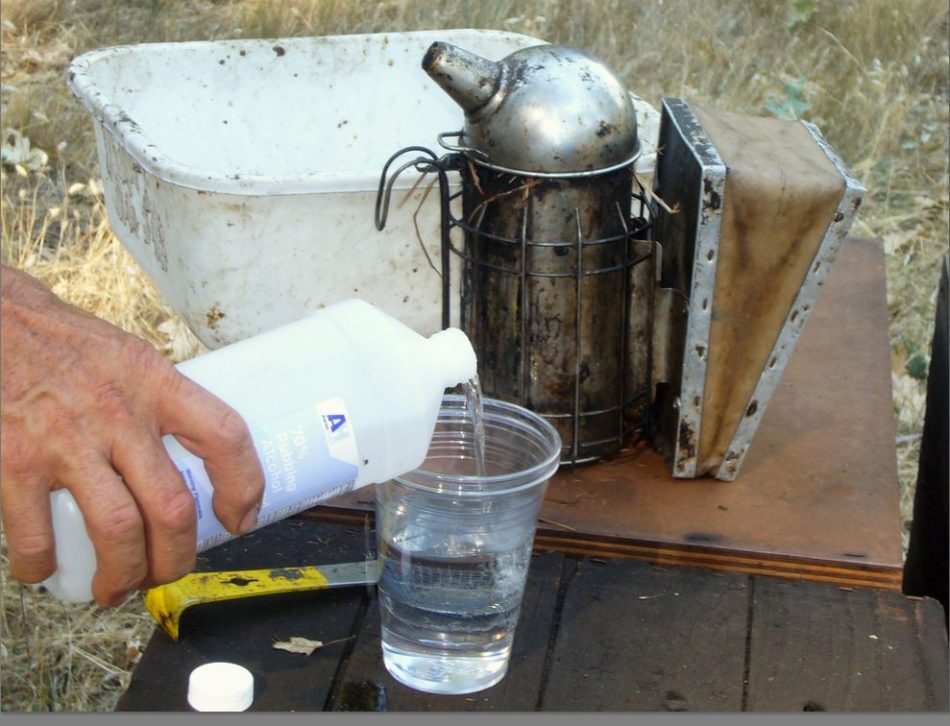
Fill the cup about 3/4ths stuffed with 91% rubbing alcohol: Replace: We’ve discovered that Daybreak Extremely dishwashing liquid, diluted to 1 Tbl per half gallon of water, works even higher than alcohol.
Now you want some nurse bees to pattern. Sure, you’ll sadly must sacrifice ~300 bees, however notice that in a typical hive, roughly 1000 bees die of previous age every day. The 300 bees are a small sacrifice with a purpose to save the lifetime of your complete colony!
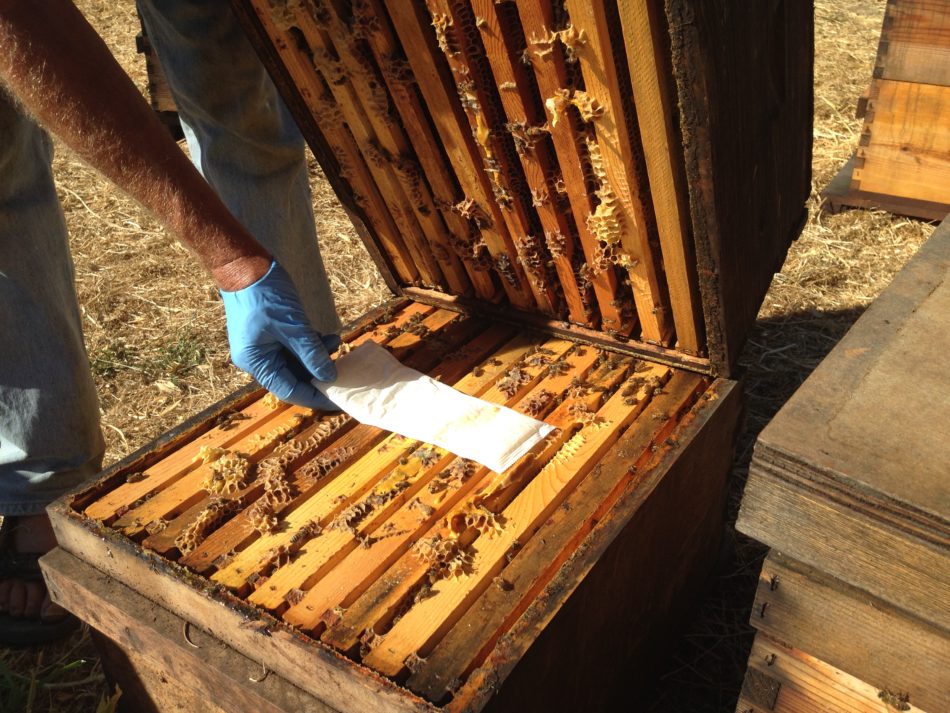
Nurse bees are scattered all through the hive, however totally on frames with brood or beebread. With the intention to keep away from harming the queen or disturbing the broodnest, merely take your bee pattern from a body from the higher brood chamber, to the aspect of the broodnest:
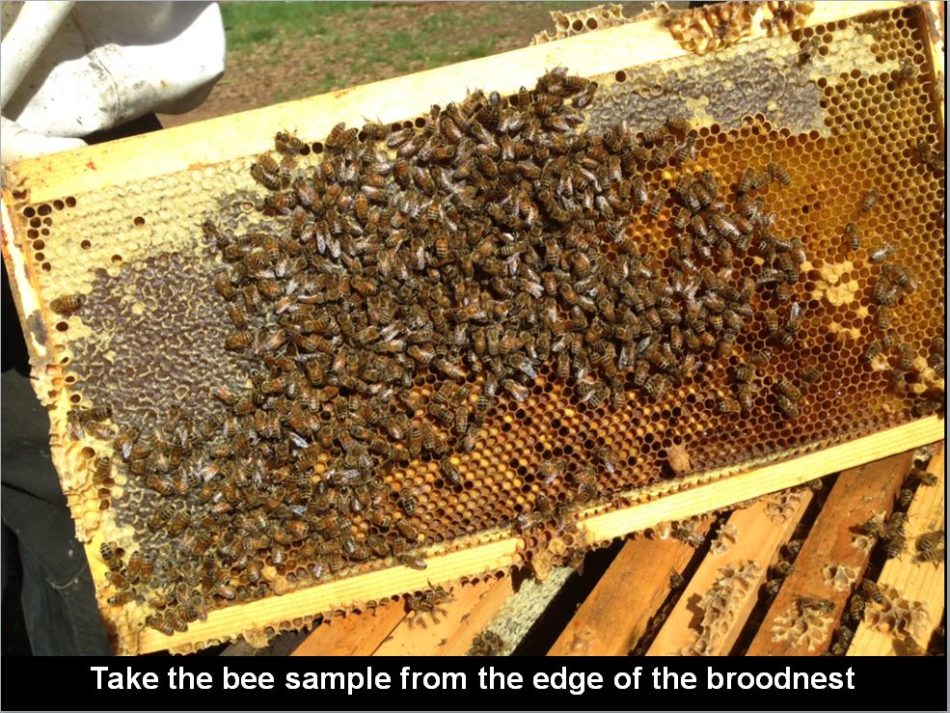

The above body is crammed with beebread, upon which solely nurse bees feed. This can be a excellent body from which to take your pattern.
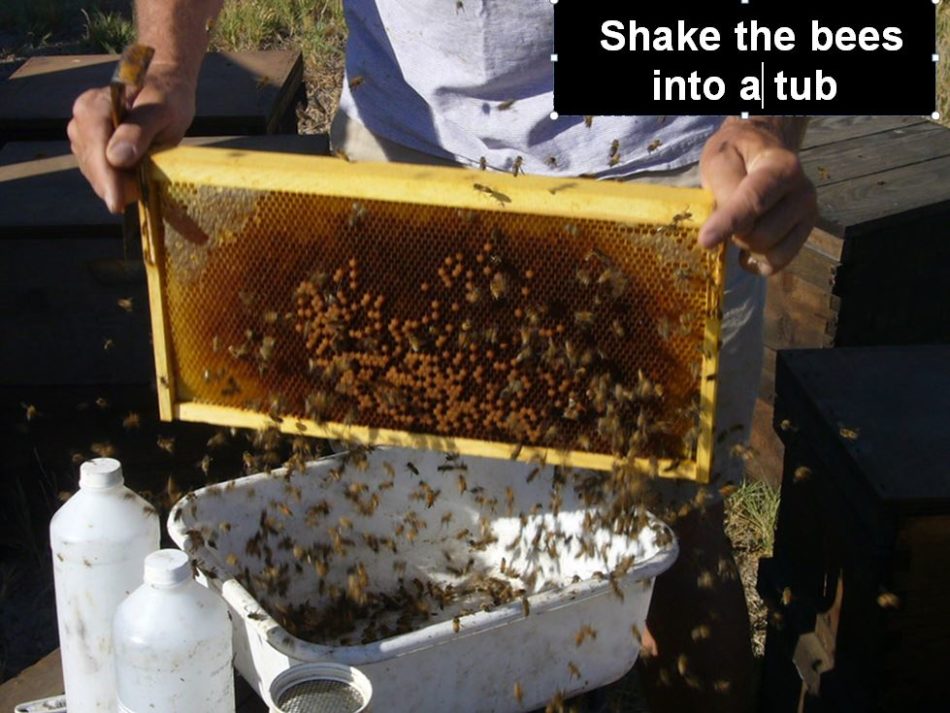

Shake the bees off the body into the bathtub–one body’s value of bees is often loads.
Now say the magic phrases: “Outdated bees fly off!” The older bees will instantly reply to your command and fly house, leaving solely the nurse bees, which is able to briefly unfold right into a single layer, during which it’s straightforward to identify the queen, ought to you will have by accident collected her. Though noisy, the bees flying off will not be in any manner inclined to sting–we do dozens of those shakes a day, and by no means have a bee try and sting us.
The younger bees remaining within the tub are utterly non-defensive, and if you want, will be gently scooped up into your hand, and poured gently from hand at hand (I usually do that at subject demonstrations to point out that younger bees hardly ever sting, until you squeeze them):
A mite wash does require the sacrifice of ~300 employees. As a lot as any of us hate to kill a single bee, the truth is, that from midsummer on, a typical colony of bees is shedding greater than 1000 employees a day to pure attrition, so a 300-bee sacrifice is a small worth for a colony to pay with a purpose to be saved from varroa. Remember that any employee within the colony would unhesitatingly sacrifice itself to learn the colony as an entire.
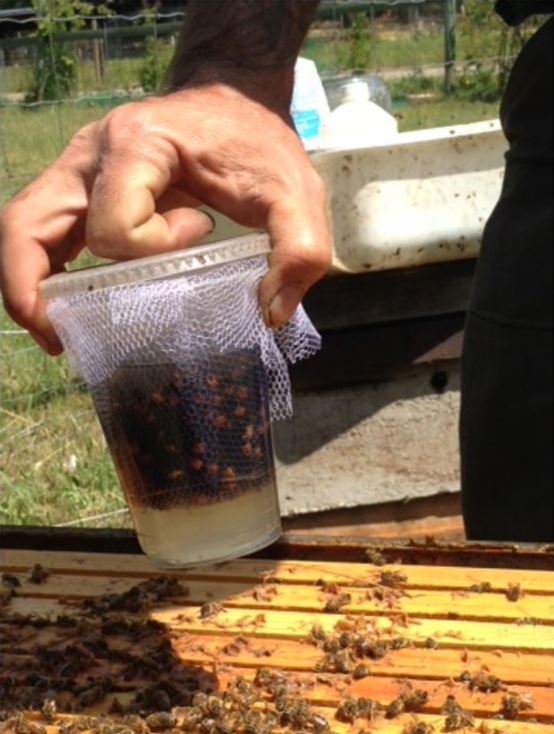
Tip the bathtub on edge and faucet the bees down right into a pile, then flip the bathtub and use the measuring cup to scoop upward to fill it overflowing with bees.
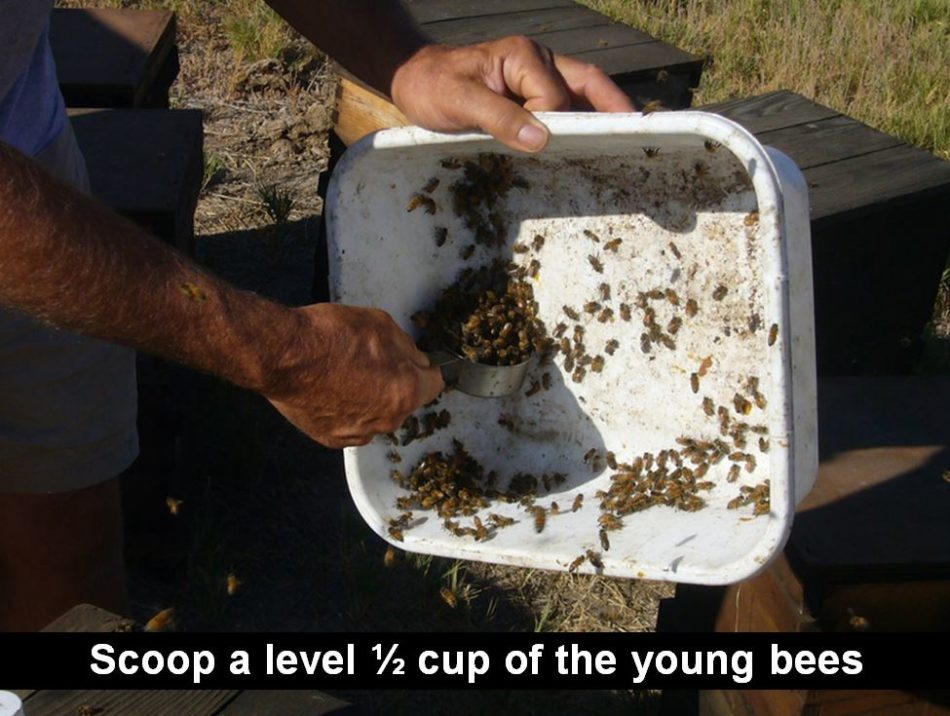

You possibly can then use your finger to degree the bees off for an actual half cup pattern. I do that a whole bunch of occasions a season, and have by no means been stung within the finger:
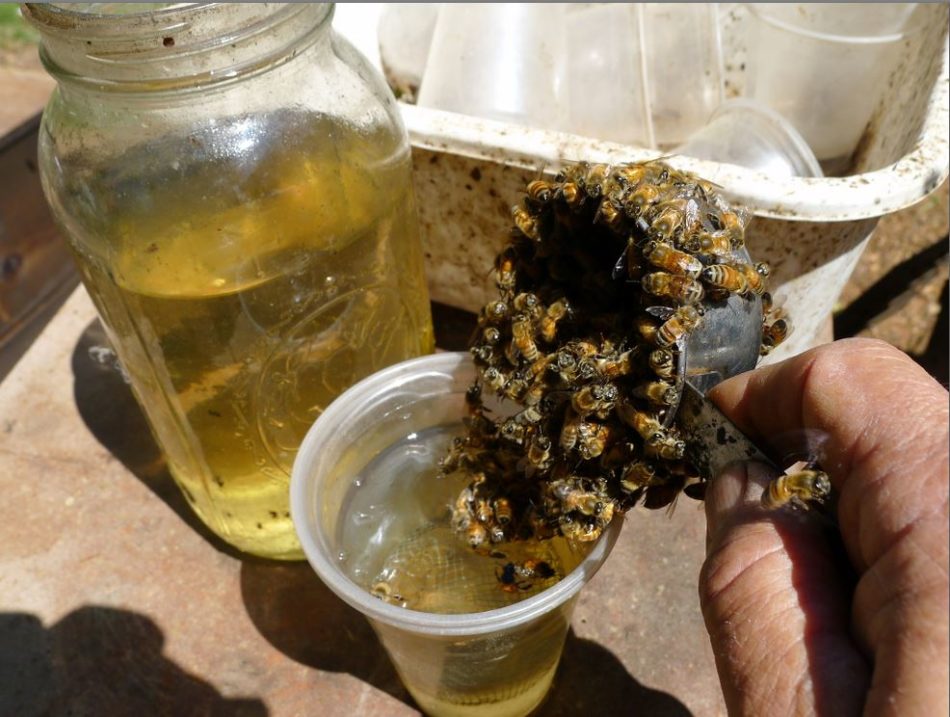
Rapidly dump the bees into the alcohol earlier than they fly out of the cup:
It helps to right away cowl the bees floating on the alcohol with the underside of the cup till they’ve submerged. All of them rapidly and humanely die. After the wash, dump the lifeless bees on the bottom and the evening critters will eagerly eat them. Or you need to use them to test for nosema beneath the microscope.
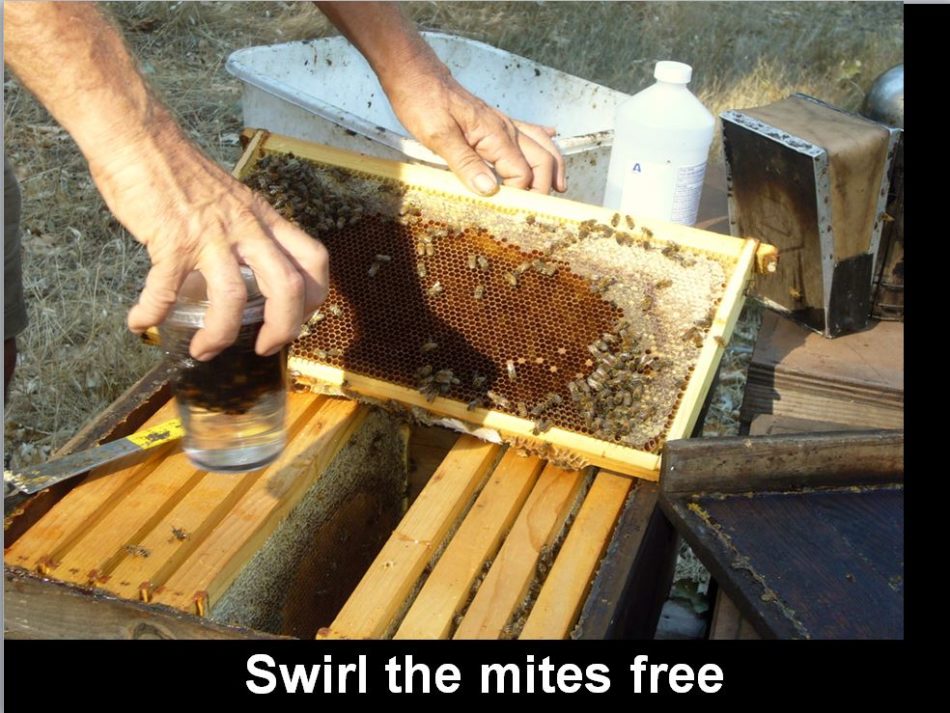
Add alcohol if essential to have 1/4″ of alcohol above the bees, with a purpose to permit them to tumble as you swirl the cup. Snap the lid onto the higher cup, and swirl the cup with a small, straightforward round movement (fingers pointing down) such that you would be able to see the bees on the backside tumbling over each other. Mites will start to drop instantly, and most will drop by 30 seconds.
With a superb swirl, you’ll get 100% mite restoration by 45 seconds. At that time, elevate the higher cup, together with the mesh, freed from the decrease cup. You possibly can then view the decrease cup from beneath to depend the mites. They’re the dimensions of a pin head, oval, and darkish reddish-brown. There are two mites within the photograph beneath:
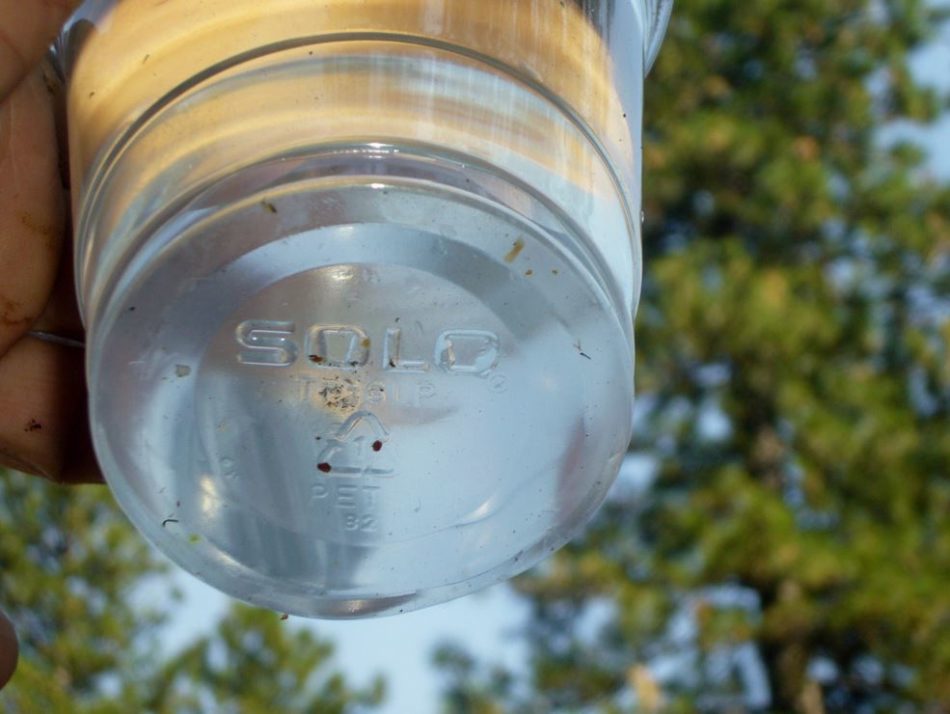

We wish to see not more than 1 mite early within the spring, no more than 3 or 4, in June, and intervene with some form of therapy if the depend goes above 6 (at most 8 mites/wash in September). Replace, with detergent fairly than alcohol, you need to depend from the underside, because of the foam.
At lower than 2 mites per 100 bees (6 in an alcohol wash of 1/2 cup of bees), virus transmission by mites is just not a serious problem. At 5 per 100 (15 in a wash), some viruses start to go epidemic. At 15/100 (45 in a wash), colonies typically begin to enter a loss of life spiral. There are roughly 82 mites within the photograph beneath. This isn’t in any respect uncommon for me to see in interest beekeeper hives in late summer season. This colony appeared effective, however will collapse earlier than midwinter. With this many mites, it already is affected by a raging virus epidemic, and is sort of unattainable to save lots of.

An important occasions to pattern are early spring, after which recurrently between August 15 and the onset of winter.
Remedies for varroa management
Suggestion #1: Be proactive fairly than reactive! It’s far simpler to maintain the varroa degree down from the beginning, than to later try and carry it down as soon as the mites have overrun the colony.
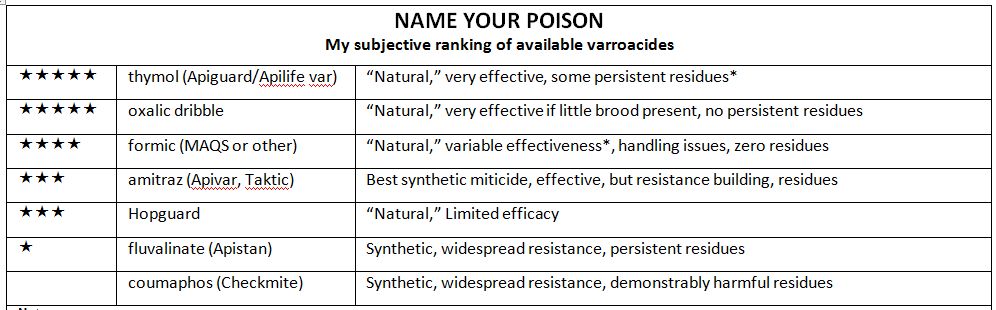
In California, with our lengthy broodrearing season, relying upon how resistant your bee inventory is to varroa, it would typically require 2-3 90% kills of the mite per season to maintain the mites beneath management. I counsel that you just ignore a lot of the data on the web, and use the well-proven efficient therapies detailed beneath (most are authorized for natural manufacturing). FWIW, though the important oils sound alluring, bees as a rule don’t like them, and they’re irritating to the colony, in addition to (apart from thymol) exhibiting poor mite management.
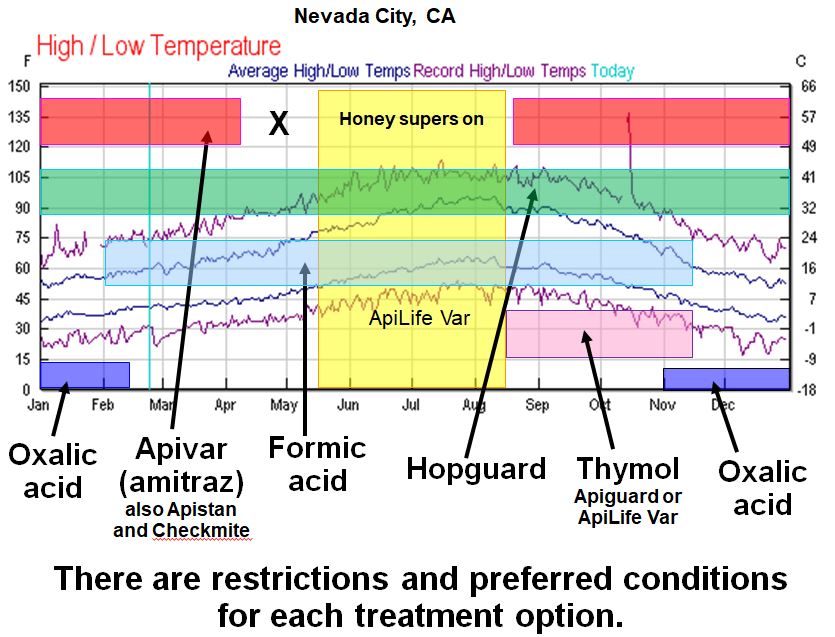
We have now excellent success with Apiguard gel (thymol) or Formic Professional (formic acid). I additionally suggest a 3.5% oxalic acid dribble (utilized precisely) earlier than Christmas (Northern Calif). I’ve detailed your seasonal selections for mite therapies beneath.
Anticipated mite reductions by therapy possibility: Use the figures beneath with Randy’s Varroa Mannequin to plan your mite administration technique.
95%: Excessive-efficacy artificial miticide, similar to amitraz utilized over a number of weeks. Not fast performing, so greatest utilized proactively, early within the season.
90%: Two 50-g Apiguard therapies at 10 days, in a rim. Greatest utilized in August, because it suppresses broodrearing.70-90% (generally much less): 2 MAQS or Formic Professional pads, or robust formic acid therapy (time launch or laborious flash). Greatest therapy for fast mite knockdown in heat climate. Can be utilized throughout honey circulation.
50% (approximate): 1 MAQS or Formic Professional pad, or single weak formic acid “knockback” therapy. Fast knockback for purchasing time, simpler on the queen.
80-90%: Hopguard 3 if colony is broodless; would require repeated functions if brood current. Can be utilized throughout honey circulation.
25%: A single powdered sugar dusting, assuming 50% drop of phoretic mites. Requires a number of and continued functions.
15-20%: Full elimination of drone brood, if executed early within the season, every elimination. Supplies some discount, however labor intensive.
40-60%: The issuance of a major spring swarm.
80-95%: Oxalic dribble or vaporization when broodless. Wonderful discount when colony is broodless, as a consequence of pure or induced brood break.
15-45%: One Oxalic dribble or vaporization in hive containing brood, proportional to the % mites of phoretic. Restricted discount when colonies include brood.
85%, 3x: Prolonged-release OA/glycerin towels or sponges; for finish end result at 45 days, enter 85% for 3 consecutive time intervals, beginning at time of utility. Not but authorized.
Extra info on therapy choices will be discovered at https://honeybeehealthcoalition.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/HBHC-Guide_Varroa_Interactive_7thEdition_June2018.pdf
Seasonally-appropriate alternative of therapy choices
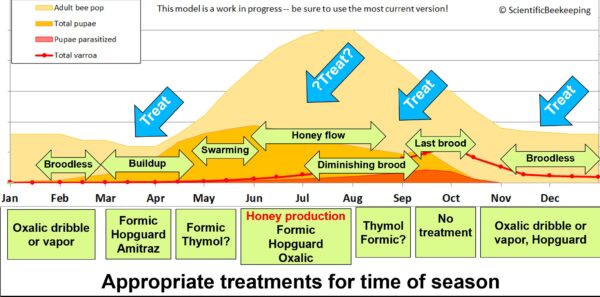
Every therapy possibility has benefits and limitations, which will be taken under consideration when formulating an annual mite administration plan.
Amitraz utilized as Apivar strips can hit the mites rising from brood, however takes 6-8 weeks to acquire full efficacy, offered that your mites don’t exhibit resistance to the product. Thus, one of the best therapy window for Apivar is both within the springtime, at the very least 8 weeks previous to the honey circulation, or instantly after pulling honey no later than mid August. Utility later within the season could also be too late.
Formic acid is the therapy of alternative for quick mite discount, and powerful functions can kill the mites inside the brood cells. Formic therapy does trigger a few 5-day brood break, however then the brand new brood seems to be nice. There may be additionally the prospect of queen loss (particularly throughout scorching climate), which may usually be prevented. Formic is acceptable in springtime, when honey is on the hive, or for severe “clear up” of high-mite hives.
Thymol is disruptive to the colony, and can trigger discount in brood rearing, and isn’t authorized to be used when honey supers are on the hive. It thus will not be applicable in springtime or fall (whenever you wish to encourage brood rearing). We discover it to be efficacious in August.
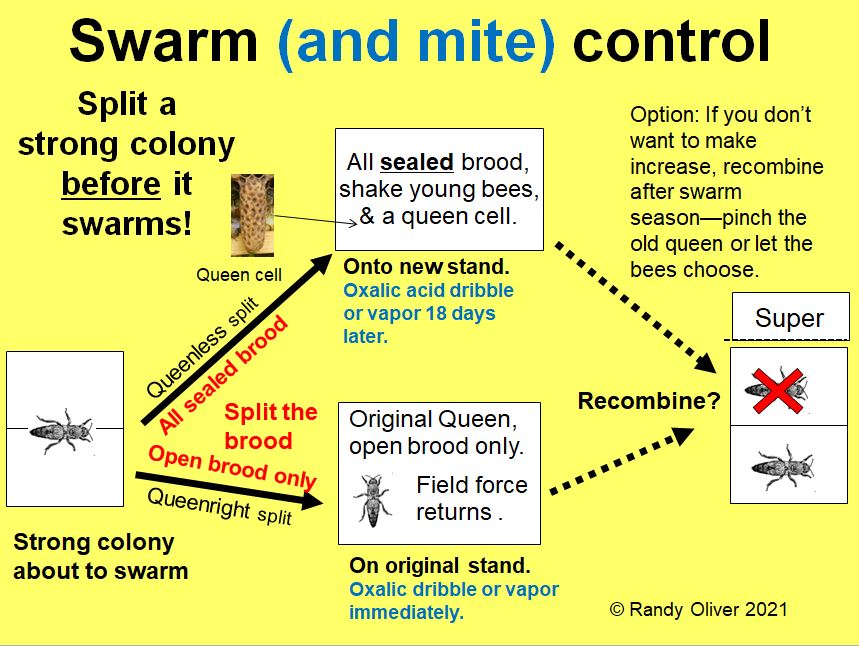
Oxalic acid could be very efficacious utilized by dribble or vapor solely when a colony is with out brood. It may be used when splitting colonies in springtime to eradicate a lot of the mites, in early winter, or with an induced brood break. Prolonged-release OA (with glycerin) is presently being registered, and will be efficacious whereas a colony has brood current.
The beekeeper can use Randy’s Varroa Mannequin to determine what number of mite reductions per yr are essential of their surroundings, and essentially the most applicable therapy sort to make use of for every discount.
Prime Bar Beekeepers
The varroa mite doesn’t care that you just’re maintaining your bees in a prime bar hive–colonies in prime bar hives are simply as prone to the mite. Except you might be working a very mite-proof bee inventory, you’ll be able to anticipate the identical form of buildup of mite populations as in Langstroth hives in late summer season, and I’ve seen loads of prime bar deadouts with clear indicators of mite overload.
Prime bar hives make mite administration a bit harder, however will be executed. For some suggestions, see: Mite administration in prime bar hives
Notes:
All miticides are poisons, however some are safer than others to each the bees and to people. The “pure” therapies are all a part of our regular food plan, and most are naturally discovered within the hive at low concentrations. I don’t hesitate to make use of them, since the good thing about controlling varroa far outweighs any well being considerations to the bees or their keeper. That mentioned, the pure therapies are all irritating to the colony, so utility directions should be fastidiously adopted. Proactive therapy means that you can use decrease (and fewer irritating) doses.
The “pure” miticides
These natural acids and important oils are authorized for natural certification. Though harder to make use of than the artificial miticides, they go away little or no residues within the combs. These are all that we’ve utilized in our operation for the reason that yr 2000. That mentioned, Apivar strips (scroll down) are very efficient for these wishing the best mite administration.
Thymol: Pure and protected (25 g of Apiguard gel accommodates the identical quantity of thymol as does 1 lb of recent thyme herb). Thymol is the one persistently efficient important oil (really a crystal at room temperature) discovered thus far. I counsel sporting disposable gloves (to remind you to not rub your eyes) . We’ve used Apiguard efficiently from 55°F to 95°F, making use of 25 g (in a lump, not unfold out) on an index card laid throughout the middle of the highest bars between the brood chambers (utility with out the cardboard can lead to extreme colony disturbance) https://scientificbeekeeping.com/the-learning-curve-part-3-the-natural-miticides/. We modify the dose in line with cluster measurement and temperature—the right dose will trigger the elimination of a handful of pupae onto the underside board by the following morning (the colony will take away them from the hive quickly afterward). I don’t suggest making use of beneath the lid, particularly in scorching climate. Repeat in per week to 10 days if mite depend is just not diminished adequately. Don’t apply if honey supers are on.

Above is 50g of Apiguard thymol gel being utilized in a 1-1/2″ rim. Hobbyists should buy it in 50-gram aluminum tins. This can be a very efficient late-summer therapy within the foothills, when you’ve pulled the honey.
Replace 2016: current exams of mine are displaying higher mite management by making use of two 50-g doses of Apiguard, 10 days aside, on prime of the hive (as per mfr’s directions) in a 1.5″ picket rim (to supply higher air circulation across the thymol). This works very properly at each day excessive temps round 85F, and can be utilized as much as 105F (however the colony will probably be considerably careworn throughout therapy). We don’t style thymol residues within the honey after therapy, however the label requires it to not be utilized with honey supers on. We get excessive efficacy with two 50-gram doses utilized 10 days aside. We get nice outcomes with Apiguard in August or September.
Thymol therapy causes the bees to maneuver the broodnest and scale back broodrearing, however after the 20-day therapy, the colony instantly recovers.
Formic acid: Pure and fairly protected, relying upon the way you deal with it (undoubtedly put on nitrile gloves; the respirator is usually pointless). The three important benefits of formic are that it successfully kills mites, is already a pure part of honey, and that it leaves zero residues within the hive. The issue is that the liquid type is considerably harmful to deal with, and getting an applicable launch of vapors is hard. The product Mite Away Fast Strips (MAQS) is essentially the most person pleasant https://scientificbeekeeping.com/an-early-summer-test-of-mite-away-quick-strips/, https://scientificbeekeeping.com/miticides-2011/. Works greatest in doubles with out supers. A single-strip therapy offers respectable mite “knock again.” A half strip works for singles with at the very least 5 frames of bees. Utilized in doubles at full dose (two strips) in summer season, we lose about 1 queen out of 25. Mite kill will not be constant, so test again. MAQS might trigger the lack of poorly-performing queens when utilized at each day excessive temps above 85F.
Making use of a single MAQS. We use this for mite knock again whereas honey supers are nonetheless on. I choose the brand new Formic Professional strips over MAQS.
Tip for interest beekeepers: to keep away from queen loss, briefly take away the queen from the hive throughout therapy– to a cage indoors, or to a two-frame nuc. Then you’ll be able to blast the hive with formic for an efficient mite kill, and return the queen after therapy (after 24 hrs with formic flash, after 5 days with MAQS).
Oxalic dribble: Pure and protected (the quantity used is equal to that in a 3½-oz serving of spinach). This product is offered at any ironmongery shop as Wooden Bleach. Comply with the blending instructions at https://scientificbeekeeping.com/oxalic-acid-treatment-table/ precisely, as there’s solely a small margin of security to the bees. The oxalic syrup could be very protected to deal with, however care must be taken to not splash it into your eyes. The therapy is by far best if the colony is broodless. Greatest use is for a single utility in November, or earlier if the colony has shut down broodrearing. You too can apply in summer season—3 functions, per week aside. Wonderful for “cleansing up” nucs within the spring https://scientificbeekeeping.com/simple-early-treatment-of-nucs-against-varroa/.
Making use of oxalic acid dribble, a simple option to management varroa, offered that there’s little or no sealed brood within the hive.
Others are utilizing oxalic vaporization, which may additionally give excellent outcomes, however has operator issues of safety–ensure to not breathe the vapor!
Pastime beekeepers can create an induced brood break by caging the queen for 12 days, then releasing her, and treating the hive with oxalic dribble or vapor 6-7 days later (day 18-19 after first caging). This can be a very cheap and efficient option to management varroa. Even higher is to make use of queen excluder division boards to restrict the queen for 14 days to a single “mite lure” body.
A house-made queen excluder division board. Use two, plus a full queen excluder, to restrict the queen to a single body.
MITE CONTROL USING A 14-DAY BROOD BREAK WITH OXALIC DRIBBLE
- Day 1: Confine the queen to 1 “varroa lure” body, utilizing queen excluder dividers.
- Day 14: Launch the queen.
- Day 21: Take away the varroa lure body and dribble the colony with oxalic acid.
See additionally “How one can kill three birds with one stone” beneath.
Replace Could 2017: I’m presently testing OA/glycerin extendend launch towels, which seem very promising See Oxalic Store Towel Updates
Hopguard: this current addition to the arsenal is totally pure, not surprisingly tasting like bitter, concentrated hops https://scientificbeekeeping.com/miticides-2011/. You’ll wish to deal with it with disposable gloves as a consequence of its messiness. Its utility and effectiveness are much like oxalic acid, however it’s extra pricey. The brand new Hopguard II strips are efficient in nucs, packages, or broodless colonies; simply ensure to not immediately hit the queen with the strip whenever you insert them.
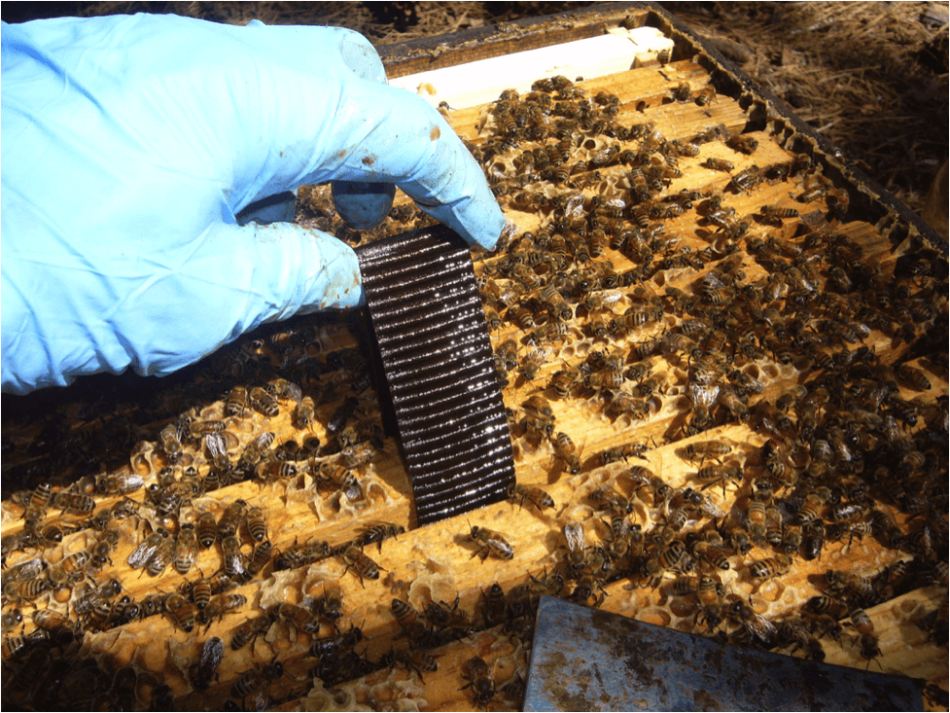

The brand new Hopguard II strips maintain rather more lively ingredient, and launch it over an extended time frame. These are useful for nucs (for which thymol and formic could also be too tough). You might must repeat therapy.
The artificial miticides
Amitraz: Industrial U.S. beekeepers have used the agricultural product Taktic, typically combined with oil or shortening, for numerous years with constant success (though this observe is against the law). Apivar strips are an enchancment, being authorized, in addition to delivering a diminished and safer dose over 42 days, leading to excessive efficacy of kill, and fewer residues within the hive. The strips, nevertheless, don’t trigger a fast kill, so could also be best in both spring (utilized at the very least 42 days earlier than the honey circulation), or in fall if mite ranges will not be too excessive, and there’s sufficient time earlier than chilly climate units in. I gave Apivar solely three stars because it does go away a residue, which current research counsel might have an effect on sperm viability within the queen and produce other sublethal results on the bees, in addition to the EPA’s authentic considerations about its security to people. There may be additionally proof that some mite populations have developed resistance to the lively ingredient.
Apivar is utilized on the charge of 1 strip per 5 frames of bees. It’s slow-release, and requires 8 weeks for full efficacy, so is greatest utilized in springtime. This artificial miticide can also be utilized in tick collars for canines. It’s efficient, particularly when utilized within the spring (a single strip is nice for nucs or packages, and displays few adversarial results upon the colony.
Fluvalinate and Coumaphos: These first-generation artificial miticides (together with the off-label use of agricultural merchandise containing the lively components) rapidly bred for resistant mites, and contaminated your complete U.S. beeswax provide. I can not suggest their use.
Our typical mite administration regime in Grass Valley is as beneath:
Replace November 2022
Remedy Recommendations by Season
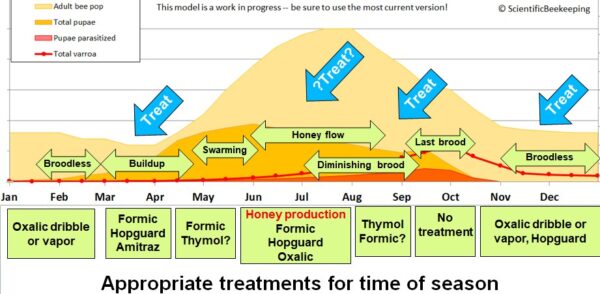
Every form of mite therapy product is best suited for various occasions of the yr. Beneath are what we’ve discovered to work properly within the Sierra Foothills–the place we’ve a brief brood break throughout chilly winter, early spring buildup, scorching, dry summer season, little pollen after mid July.
Midwinter--generally go away colonies alone
Early spring–oxalic dribble* earlier than there’s a lot sealed brood; formic acid, or Apivar (amitraz strips–the best and best, however should be eliminated previous to gathering honey). Feed pollen sub if poor foraging climate.
Mid spring–drone brood elimination, splitting with induced brood break and requeening, coupled with oxalic dribble*. Formic Professional–half or full dose. Doubtless too late for Apivar.
Late spring–apply extended-release OA/glycerin therapy on cellulose towel (if authorized in your nation). Formic Professional–half or full dose.
Late June–test mite ranges whereas honey supers are nonetheless on; deal with with formic acid if indicated Formic Professional–half or full dose.
Mid August (there is no such thing as a benefit to us for broodrearing presently)–50 g Apiguard thymol gel, 10 days to 2 weeks aside, in a 1.5-inch rim above the brood nest (or two 25-g functions between the brood chambers). Exhausting formic blast to hives with excessively excessive mite counts. Apivar strips (that is the newest utility date for satisfactory mite management earlier than autumn).
Early September by October–Mite management ought to have been accomplished by now; if not, use Formic Professional for a fast therapy. Feed pollen sub (and syrup if essential) to stimulate the rearing of wholesome brood that can type the winter cluster. As a consequence of potential mite immigration from different hives, monitor mite ranges, and deal with with OA* or Formic Professional–half or full dose– if essential.
Late November/December (because the final sealed brood emerges)–dribble with OA*. OA vaporization additionally an possibility.
*We choose the oxalic dribble in 40% glycerin (Google my “Oxalic Acid Remedy Desk”), however OA vaporization will give related outcomes, with slow-release vaporizers presumably being simpler.
Fomic acid particulars
In late summer season, when colonies are stuffed with brood, and mite ranges get excessive, we use formic acid. I’m experimenting with totally different utility strategies, looking for ones which can be protected for the applicator, and that don’t trigger queen loss in scorching climate.
The great thing about formic acid is that it penetrates the cappings if utilized at a excessive sufficient focus, leaves no residues within the hive or honey, and provides a colony a brand new lease on life (the next brood patterns are sometimes lovely).
Right here’s what we’ve discovered to work for our double-deep Langstroth hives (could also be totally different in case your beekeepers have totally different hive configurations):
- A single MiteAway Fast Strip (MAQS) between the brood chambers. About 50% mite discount, however no queen loss.
- Two MAQS between the brood chambers, however with the higher chamber shifted entrance or again to go away a 2 cm area for air flow. There could also be some lack of already-failing queens.
- Prime formic flash, 65% formic utilized by a fume board. 30 mL will give a mite knock again, 90 mL will give close to full mite kill, however may even kill some queens in scorching climate. The beekeeper can all the time take away the queen to a cage or a nuc in a single day whereas doing the flash.
- The Nassenheider formic applicator additionally works, however is extra difficult.
- For actually high-mite hives, we cut up all the way down to single containers, and apply 300 mL of 65% formic absorbed into some cellulose, positioned in a plastic bag with round 50 paper-punch holes. This may kill all of the mites within the field, however not kill the sealed brood or grownup bees (anticipate to see about 50-100 lifeless adults the following day). It would kill a big share of queens if they aren’t eliminated. The therapy takes a few week, however for those who add a brand new queen again, the colony will rapidly rebound like new.
- For nucs, you need to restrict the discharge charge of the formic. We use one-half of a MAQS, set on the highest bars, with the highest of the strip tightly coated by both the hive cowl or plastic. This limits formic launch vastly–it takes properly over per week for the strip to go dry.
For additional info, I counsel the next articles:
https://scientificbeekeeping.com/sick-bees-part-12-varroa-management-getting-down-to-brass-tacks/
Again to the hive: including one other brood chamber
As soon as the bees have drawn out all of the combs within the first brood field, you’ll be able to add the second brood field (chances are you’ll want to add a drone body for mite trapping).
Don’t combine drawn combs with the muse; simply add 10 frames of foundation-this will produce the straightest combs.
We have now our greatest luck at drawing basis by including full containers of 10 frames immediately over the brood of robust (at the very least 10 frames coated with bees) rising colonies throughout a robust nectar circulation.
Maintain feeding the colony till all of the combs are drawn out. At this level, the brood chamber is full (assuming a double deep brood chamber), and it is best to discontinue feeding.
A wholesome colony will usually create drone comb between the 2 brood chambers in spring. All the time test such uncovered brood instantly for the presence of varroa, as it’s a respectable indicator of brewing issues.
If the colony fails to maneuver up onto basis in an added field, it’s typically as a consequence of an absence of nectar circulation. In that case, hold feeding sugar syrup. Bees is not going to draw basis until they’re “whitening wax” as a consequence of intense feeding or an intense nectar circulation. It takes a minimal of two gallons of heavy syrup to attract the wax on 10 deep combs, and one other 5 gallons to fill them with sugar “honey” for winter shops.
Including Honey Supers
As soon as the colony has crammed two brood chambers (this will not happen in your first yr), you’ll be able to then add a queen excluder (I extremely suggest) and honey supers.
Don’t hassle including basis until you see white wax. However all the time add extra combs for those who do!
Queen Excluders
Bees don’t like to attract basis positioned above an excluder (not an issue in case you are including drawn comb, which you’ll sadly not have accessible your first season). To encourage bees to work by the excluder, I counsel “reversing” the brood chambers if there’s a band of honey throughout the highest of the higher combs. This maneuver will place brood immediately beneath the excluder, which inspires the bees to work upward.
Remember that bees will not draw basis until they’re producing white wax. This rule applies much more emphatically in case you are making an attempt to get them to work by an excluder onto basis.
There’s a main benefit of maintaining your honey supers freed from brood cocoons–wax moth can not develop on saved “white” combs freed from brood cocoons or beebread (not sufficient protein). Through the use of queen excluders, you’ll be able to hold your honey combs freed from brood cocoons, and thus eradicate the storage drawback from wax moth.
Getting a Style of Honey
OK, chances are you’ll not get a full honey crop your first season, however you’ll be able to at the very least steal slightly from the bees as long as you substitute it by feeding them heavy (2:1 sugar:water) syrup earlier than cool climate units in.
Let’s say that the primary brood field is full, and now the honeyflow is beginning, and also you’d actually prefer to get slightly honey the primary yr. Simply placed on the second brood field, and cease feeding syrup. Let the bees work up and fill the field with brood and honey. As soon as the honeyflow’s over (often as soon as blackberry stops blooming on the finish of June), you’ll be able to pull out frames of honey and do a “scrape extraction.” Use a tablespoon to scrape the honey off the muse right into a nylon stocking hung in a gallon jar, then return the scraped body to the hive, and resume feeding till the bees draw it out once more. They’ll winter simply effective on honey constructed from sugar syrup.
Supering your Hive for Honey Manufacturing
I like queen excluders–they will let you hold the queen out of your honey supers. The world’s largest crops of honey (in Australia) are all produced by queen excluders.
One of the vital frequent complaints is the “my bees wouldn’t undergo the queen excluder to attract basis.” Bees gained’t achieve this till each single cell of drawn comb beneath the excluder is filled with nectar–solely then will they work basis, and as I discussed above, they gained’t draw basis until there’s a very heavy nectar circulation on. Bees are also adversarial to crossing a strong “honey band” beneath the excluder. A Tip: you’ll be able to encourage them to maneuver by the excluder by rearranging your brood containers or frames in order that there are frames of brood proper as much as the queen excluder.
Late-Summer season Administration and Varroa Management
Your colony will typically attain its most measurement round July 1, and get considerably smaller in the course of the late summer season and fall. Within the foothills, there’s sometimes a pollen dearth from early July by October, and the colony will reduce its broodrearing. That is good, because it reduces varroa copy. Use this window of alternative to manage varroa in August (Apiguard thymol gel works very properly).
After you’ve bought varroa beneath management, chances are you’ll then want to present the hive with high-quality pollen sub as beneath:
Winter Preparation
Colonies winter greatest (within the foothills) in two deep brood chambers or equal, with a complete weight (primarily as a consequence of honey) of about 130 lbs (you want at the very least two fingers to tip the hive). If the hive is just not heavy by the tip of September, feed heavy sugar syrup till it’s.
In case your apiary is situated in a dry space of the foothills, there will not be sufficient pollen to maintain late summer season broodrearing–colonies in these areas vastly profit from late summer season feeding with pollen complement. Any of the top-tier pollen dietary supplements work–for those who don’t see pollen beebread in an arc above the brood, the colony is probably going hurting for protein. We sometimes feed every colony a number of kilos of pollen complement throughout August by October. This will not be essential for those who stay on the town or in an irrigated space.
The perfect indicator of protein standing is how a lot jelly the nurse bees are feeding to the younger larvae. Larvae fed generously with jelly are known as “moist brood.”
When a colony suffers from protein deficiency, the nurses will reduce on the quantity of jelly that they feed to larvae. See the photograph beneath for “dry” brood.
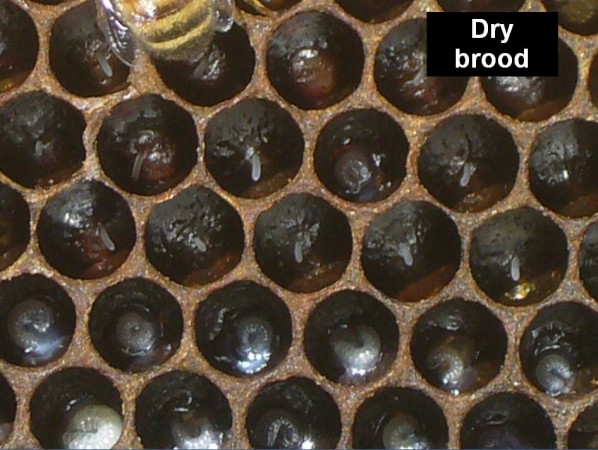 There are eggs within the middle cells; larvae being given minimal jelly within the cells beneath. Once we see such “dry” larvae, we instantly feed patties of pollen substitute (see Comparative Check of Pollen Subs).
There are eggs within the middle cells; larvae being given minimal jelly within the cells beneath. Once we see such “dry” larvae, we instantly feed patties of pollen substitute (see Comparative Check of Pollen Subs).
There’s a commerce off relating to the autumn feeding of your hives. Colonies which can be robust and properly fed in fall winter properly, however will then even be robust in spring. They’ll then wish to swarm. Escaped swarms later develop into “mite bombs” that can come again to hang-out you. So for those who construct your colonies up by feeding, please then handle them to forestall swarming the following spring–this may assist the beekeeping neighborhood general.
Rust fungus spores
Bear in mind that within the Sierra foothills, in late summer season the bees could also be tricked by a fungus into gathering their spores as a substitute of nutritious pollen. The blackberry rust fungus produces sweetened fluorescent-orange spores that the protein-desperate bees will collect and retailer as beebread–beneath:
This shiny orange beebread consists practically totally of rust fungus spores. Colonies rapidly go downhill on this food plan–be aware the spotty brood sample. Don’t let this beebread idiot you! If we see this occurring, we give the hives two rounds of 2-3 lbs of top quality pollen sub:
Should you stay on the town, there’ll seemingly be sufficient pollen to maintain your colonies wholesome throughout late summer season. Quite the opposite, in dry rural areas, colonies can go downhill as a consequence of lack of pollen (and particularly if they’re gathering rust fungus spores). Feeding pollen sub (above) can rejuvenate these colonies. However remember that its a commerce off–rising broodrearing additionally will increase varroa copy.
It takes a good quantity of pollen sub to supply sufficient protein–about one 1-lb patty per week (you’ll be able to feed a number of kilos at one time for those who don’t have Small Hive Beetle in your space).
Winter Prep
Winter prep consists of getting the hives off the bottom and in a well-drained sunny location. It helps to cut back the doorway. A well-prepared colony (properly fed, and low mite degree) ought to want no care in the course of the winter, and can start to rebuild its inhabitants in January. An insulated cowl (similar to with 1″ of Styrofoam) will assist the colony.
Subsequent Spring and Splitting
Most robust colonies will try to breed in spring by swarming.
Should you elevate the higher field of the broodnest of a colony making ready to swarm, you’ll sometimes see swarm cells hanging from the underside bars as proven above (however there might be swarm cells elsewhere within the hive). The previous queen and a swarm might go away any time as soon as the primary cells are sealed.
There are administration strategies than can be utilized to attenuate the cues that provoke the swarm impulse (see Minimizing Swarming ). One of the vital efficient strategies is to easily cut up the colony. You possibly can cut up a robust colony in half, or make as much as 5 nucleus hives from it. Nevertheless, remember the fact that there could also be a tradeoff between later honey manufacturing and “making enhance.” Ideally, you’d take away solely sufficient bees to avert swarming, however go away sufficient for the colony to recuperate its most inhabitants simply in time for the beginning of the primary honeyflow in your space.
There may be additionally the problem of the best way to present queens to the splits–some strategies lead to a really lengthy break throughout which the colony can have no rising grownup bees–see the desk beneath:
On the whole, the extra brood that you would be able to put right into a cut up, the higher (the quantity of brood is extra vital than the quantity of grownup employees). Sometimes, make your splits with at the very least 5 frames of bees, a ripe queen cell, and a minimal of two full frames of brood. However such a cut up might not make a honey crop within the first yr. The identical cut up made with 4 full frames of brood and a laying queen, then again, can properly develop rapidly and make a honey crop, if instantly given loads of drawn comb, and fed some sugar syrup.
How one can kill three birds with one stone
You possibly can kill three birds with one stone every spring–stopping swarming, requeening, and mite management. See the graphic beneath:
By splitting your colony when it’s pondering of swarming (by utilizing both a pure swarm cell or a bought one), you need to use oxalic acid dribbles (at totally different occasions) to just about eradicate varroa from the 2 splits (by creating induced brood breaks). The small-scale beekeeper can simply handle varroa by utilizing the above or related artistic strategies of making brood breaks.
Miscellaneous
Learn all about beekeeping, however keep in mind that there is no such thing as a substitute for hands-on expertise within the beeyard with an seasoned beekeeper. Discover a mentor in your space. The simplest take a look at for selecting a mentor is to seek out somebody who persistently has further bees on the market every spring (not essentially the one who’s most strongly opinionated).
Getting a colony of bees is just not like getting a pet–you anticipate the pet to stay to previous age; this will not be the case with bees. In nature, a big share of colonies die annually. Even one of the best beekeepers might have a 3rd of their colonies die in some years. It helps to maintain a couple of colony, so that you could cut up it in spring to make up for losses.
Good luck together with your new colony—I hope you will have nice success this yr! If in case you have options as to how I can enhance these directions, please let me know!
Extra sources:
For a superb, customary, no nonsense abstract of fine beekeeping practices, see
http://www.beesource.com/sources/usda/productive-management-of-honey-bee-colonies/